arabera ourclass9u o 11 years ago
589
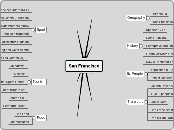
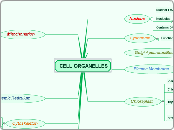
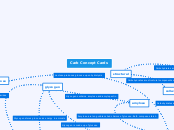
Structural Organisation Of Cells
Cells are highly organized structures with specialized components that perform distinct functions crucial for life. The endoplasmic reticulum, an extensive network of membranes, is responsible for protein production and lipid synthesis.