Common Ancestor with DNA
Bacteria
- Ester Linkage
- DNA Present
- Simple RNA Polymerase
- Formylmethionine
- Cell Wall contains Peptidoglycan
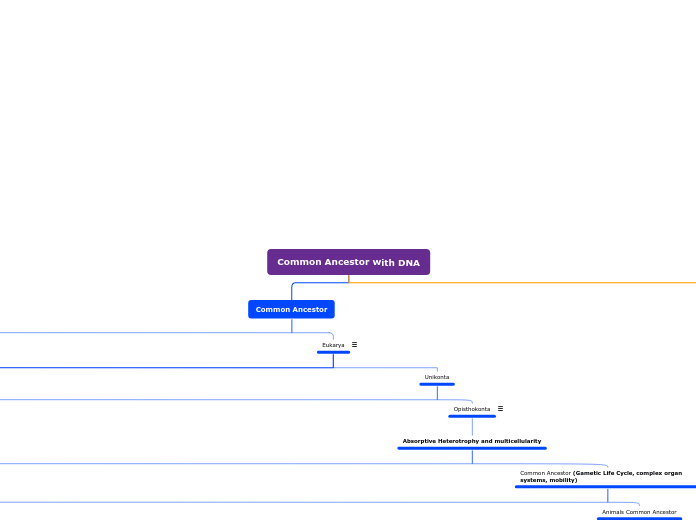
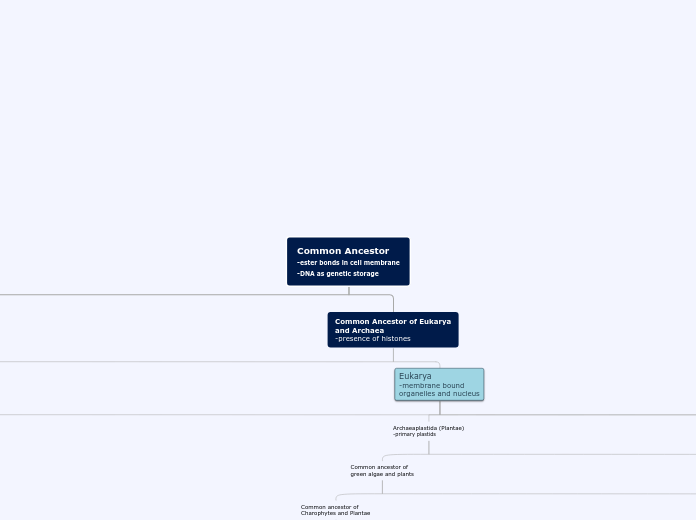
Common Ancestor
Eukarya
- Ester Linkage
- DNA Present
- Histones Present
- Membrane bound organelees
- Chromosomes located in membrane bound nucleus
- Multiple RNA Polymerases
- Methionine
- Cell wall (when present) does not contain peptidoglycan
- Membrane bound nucleus
Unikonta
Opisthokonta
- Single posterior flagellum on swimming cells
Absorptive Heterotrophy and multicellularity
Common Ancestor (Gametic Life Cycle, complex organ systems, mobility)
Animals Common Ancestor
Porifera (No Symmetry, No tissue)
Giant Barrel Sponge
Eumetazoa (Tissues)
Ctenophora
Cnidaria (Radial Symmetry, Diploblasty)
- Incomplete Digestive Tract
Anthozoa
Elkhorn Coral
Common Ancestor (Medusozoa)
Scyphozoa
Moon Jelly
Hydrozoa
Bilateria (Bilateral Symmetry, Triploblasty)
Acoela
Deuterostomia (Radial and indeterminate cleavage, blastopore becomes anus)
Chordata (Notochord, hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post anal tail)
Cephalochordata
Common Ancestor (Vertebrae, Cranium, Cartilagenous skeleton, Ectothermy)
Common Ancestor (Jaws)
Common Ancestor (Lungs or lung derivatives, Bony Skeleton)
Common Ancestor (Lobed fins)
Common Ancestor (Limbs w/ Digits)
Common Ancestor (Amniotic Egg, Endothermy)
Milk and Hair
Mammalia
- 4 chamber heart
- Double Circulation
American Black Bear
Reptilia
- 4 chamber heart for birds and crocodilians
- 3 chamber heart for lizards, snakes, and turtles
- Birds are endothermic
- Double Circulation
Green Sea Turtle
Amphibia
- 3 chamber heart
- Double Circulation
Red Eyed Tree Frog
Lungfishes
Lobe Finned Fishes
Coelacanth
Ray-Finned Fishes
- 2 chamber heart
- Single Circulation
Blue Tang
Chondrichthyes
- 2 chamber heart
- Single Circulation
Great White Shark
Agnathans
- 2 chambered heart
- Single Circulation
Lampreys
Hagfishes
Pacific Hagfish
Urochordata
Sea Peaches
Common Ancestor (Water Vascular System)
Echinodermata
- Pentaradial Symmetry in Adults
- Coelomate
- Water Vascular System
- Complete Digestive Tract
Ophiuroidea
Serpent Star
Echnoidea
Purple Sea Urchin
Holothuroidea
California Sea Cucumber
Asteroidea
Giant Sea Star
Common Ancestor (Spiral and Determinate Cleavage, blastopore becomes the mouth)
Lophotrochozoa (Trochophore larvae, lophophore)
Common Ancestor (Cephalization except for Bivalves)
Platyhelminthes
- Acoelomate
- Incomplete Digestive Tract
Tapeworms
Pork Tapeworm
Trematoda
Sheep Liver Fluke
Free Living Rhabditophorans
Common Ancestor (Trochophore Larvae)
Mollusca
- Coelomate
- Mollusks except Cephalopods have an open circulatory system
- Cephalopods have a closed circulatory system
- Complete Digestive Tract
- Mollusks have gills
Gastropoda
Golden Apple Snail
Bivalva
Soft Shell Clam
Cephalopoda
Humboldt squid
Annelids
- Coelomate
- Closed Circulatory System
- Complete Digestive Tract
Common Earthworm
Ecdysozoa (Ecdysis)
Common Ancestor (Complete Digestive Tract with Cephalization)
Arthropoda
- Coelomate
- Open Circulatory System
- Aquatic Arthropods have gills
Common Ancestor (Pancrustaceans)
Crustacea
Chesapeake Blue Crab
Hexapoda
Monarch Butterfly
Chelicerata
Southern Black Widow
Nematoda
Roundworm
Choanoflagellates
Common Ancestor (Zygotic Life Cycle, cell wall)
Fungi
Black Bread Mold
Fly Agaric (Amanita muscaria)
Amoebozoans
- Movement with pseudopodia
Slime molds
SAR Clade
Rhizaria
foraminiferas
radiolarians
Common Ancestor of Stramenopila and Alveolata
Alveolata
- Membranous vesicles on cell membrane
Dinoflagellate
Stramenophila
- Tripartite flagellar hair
- Secondary Plastids
Giant Kelp
Diatoms
Excavata
- Feeding Groove
- Secondary Plastids
euglenoids
Archaeplastida
Common Ancestor (Chlorophyll a & b, b-carotene cellulose rich cell walls)
Common Ancestor (Ring-shaped cellulose synthesizing proteins phragmoplast)
Plants (Sporic Life Cycle, embryo, gametangia, sporangia, apical meristems, and dessiccation resistant spores)
Common Ancestor (xylem and phloem, dominant sporophyte, thick waxy cuticle, leaves, stomata and lignin)
Common Ancestor (megaphylls)
Common Ancestor (Seeds, Ovules, Wood, Heterospory, Pollen)
Angiosperms
- Have pollen
- Have a seed
- Have a fruit
- Have flowers
- Have an endosperm
- Are heterospory
- Have wood
- Have ovules
- Have ovaries
(flowers, ovaries, fruit, and endosperm)
White Water Lily
Southern Magnolia
Gymnosperms
- Have pollen
- Have a seed
- Do not have a fruit
- Do not have flowers
- Do not have an endosperm
- Are Heterospory
- Have wood
- Have ovules
- Do not have ovaries
Bald Cypress
Scots Pine
Monilophytes
- Sporic Life Cycle
- Has Embryo
- Has Dessication-resistant Spores
- Has Apical Meristem
- Has Gametangia, sporangia, and lignin
- Uses xylem/phloem
- Has true leaves and megaphylls
- Does not have lycophylls
- Sporophyte is dominant
- Has a thick waxy cuticle and stomata
Eastern Marsh Fern
Lycophytes
- Sporic Life Cycle
- Has Embryo
- Has Dessication-resistant Spores
- Have Apical Meristem
- Have gametangia, sporangia, and lignin
- Use xylem/phloem
- Has true leaves and lycophylls
- Does not have megaphylls
- Sporophyte is dominant
- Has a thick waxy cuticle and stomata
Fan Clubmoss
Hornworts
- Sporic Life Cycle
- Has Embryo
- Has Dessication-resistant Spores
- Have Apical Meristem
- Have gametangia and sporangia
- Do not have lignin
- Uses diffusion/osmosis
- Has no true leaves
- Does not conatain lycophylls or megaphylls
- Gametophyte is dominant
- Does not have a thick waxy cuticle or stomata
Field Hornwort
Mosses
- Sporic Life Cycle
- Has Embryo
- Has Dessication-resistant Spores
- Has Apical Meristem
- Has Gametangia and sporangia
- Does not have lignin
- Uses diffusion/osmosis
- Has no true leaves
- Does not contain lycophylls or megaphylls
- Gametophyte is dominant
- Does not have a thick waxy cuticle or stomata
Woolly Feather Moss
Liverworts
- Sporic Life Cycle
- Has Embryo
- Has Dessication-resistant Spores
- Have Apical Meristems
- Have Gametangia and sporangia
- Does not have lignin
- Uses diffusion/osmosis
- Has no true leaves
- Does not contain lycophylls or megaphylls
- Gametophyte is dominant
- Does not have thick waxy cuticle or stomata
Common Liverwort
Charophytes
- Zygotic Life Cycle
- No Embryo
- Does Not have Dessication-resistant spores
- No Apical Meristem
- Does not have a gametangia, sporangia, or lignin
- Uses Diffusion/Osmosis
- Has no true leaves
- Does not contain lycophylls or megaphylls
- Gametophyte is dominant
- Does not have a thick waxy cuticle or stomata
Zygotic Life Cycle
chlorophytes
rhodophytes
Archaea
- Ether Linkage
- DNA Present
- Histones Present
- Multiple RNA Polymerases
- Methionine
- Cell Wall (when present) does not contain peptidoglycan