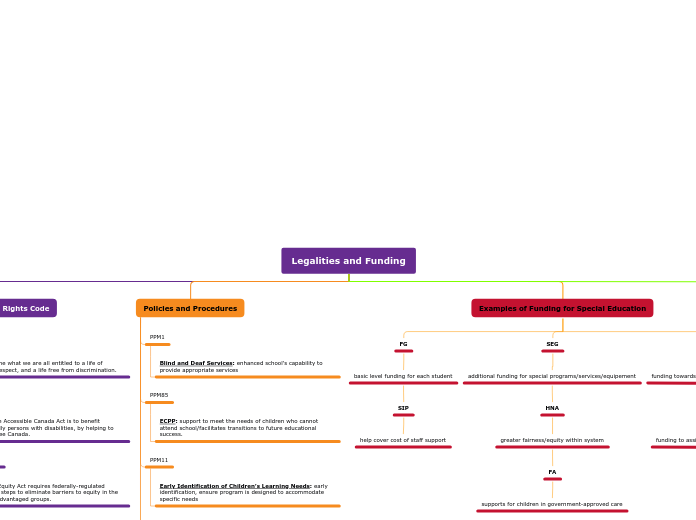
Legalities and Funding
SEAC
Ministry of Education is responsible for providing the regulatory and policy framework within which school boards exercise their responsibility.
SEAC makes recommendations to their board on any matter affecting the establishment, development and delivery of special education programs and services for exceptional students.
SEAC participates in annual budget process.
SEAC reviews financial statements.
Examples of Funding for Special Education
SEPPA
funding towards special education supports
SEA
funding to assist with cost of equipment
SEG
additional funding for special programs/services/equipement
HNA
greater fairness/equity within system
FA
supports for children in government-approved care
FG
basic level funding for each student
SIP
help cover cost of staff support
Policies and Procedures
Supporting Transitions for Students with Special Education Needs: Individualized transition plans that reflect a student’s strengths and needs
PPM156
PPM11
Early Identification of Children’s Learning Needs: early identification, ensure program is designed to accommodate specific needs
PPM85
ECPP: support to meet the needs of children who cannot attend school/facilitates transitions to future educational success.
PPM1
Blind and Deaf Services: enhanced school's capability to provide appropriate services
Canadian Human Rights Code
Pay Equity
Closing the gender pay gap and improving social services for women in vulnerable circumstances are a must.
Housing
The Federal Housing Advocate promotes and protects the right to housing in Canada.
Employment Equity
The Employment Equity Act requires federally-regulated employers to take steps to eliminate barriers to equity in the workplace for disadvantaged groups.
Accessibility
The purpose of the Accessible Canada Act is to benefit everyone, especially persons with disabilities, by helping to create a barrier-free Canada.
Human Rights
Human rights define what we are all entitled to a life of equality, dignity, respect, and a life free from discrimination.
United Nation's Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities
Convention elaborates in detail the rights of persons with disabilities and set out a code of implementation”.
As a change of perceptions is essential to improve the situation of persons with disabilities, ratifying countries are to combat stereotypes and prejudices and promote awareness of the capabilities of persons with disabilities
States are to ensure equal access to primary and secondary education, vocational training, adult education and lifelong learning.
Persons with disabilities have equal rights to work and gain a living.