arabera Fernanda Avila 4 years ago
768
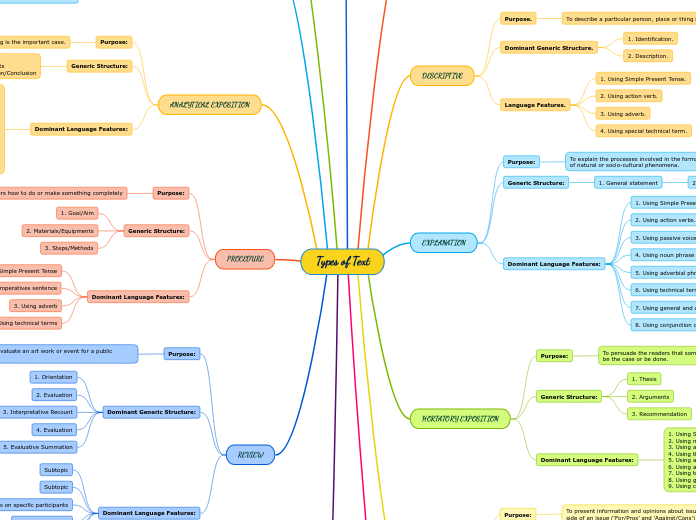
Types of Text
Analytical exposition aims to highlight the importance of a particular issue, employing a structured format that begins with a thesis, followed by arguments, and concludes with a reiteration.
arabera Fernanda Avila 4 years ago
768

Honelako gehiago
2. Description
2. Event(s).
3. Reorientation.
2. Explanation
3. Closing
4. Reorientation (optional).
3. Resolution.
2. Complication.
1.Orientation.