Child Development
Related image
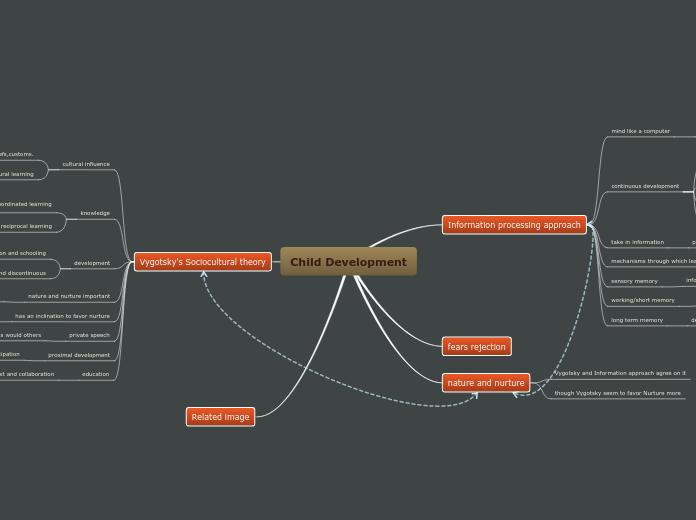
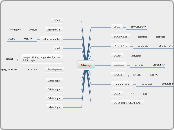
Vygotsky's Sociocultural theory
education
social context and collaboration
instruction,appropiate guidance
proximal development
intersubjectivity,scaffolding,guided participation
private speech
child talks to self as much as would others
has an inclination to favor nurture
socio and cultural contribution to children's thinking
socially formed mind of a child
nature and nurture important
heredity and dialogues with society are both important
development
continuous and discontinuous
language acquisition and schooling
vary from culture to culture
knowledge
reciprocal learning
coordinated learning
cultural influence
sociocultural learning
values, beliefs,customs.
nature and nurture
though Vygotsky seem to favor Nurture more
Vygotsky and Information approach agree on it
fears rejection
Information processing approach
long term memory
declarative,procedural and imagery memory
stored memory
working/short memory
information maintained
sensory memory
information gathered
mechanisms through which learning occurs
take in information
processes information
output processes
response
continuous development
perception, labelling and meaning
information expands in various ways
development stages
children continually improve
responds to environment
mind like a computer
information flow
input,stored and processed