Genetic Disorders
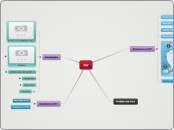
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Treatment.
There is no definitive cure, but it can be managed with medications, physical and occupational therapies, treatments for complications, and, in some cases, surgery.
It is generally detected in early childhood. Signs and symptoms usually appear between the ages of 2 and 5.
They may develop respiratory and cardiac complications.
They usually lose the ability to walk during adolescence.
Symptoms include progressive muscle weakness, which typically begins in the legs and then affects the arms and torso.
DMD originates from mutations in the DMD gene, which is responsible for encoding the dystrophin protein. It is located on the X chromosome, specifically in the Xp21.2 region.
It is a recessive genetic disease; it is progressive and severe, and it belongs to the group of muscular dystrophies.
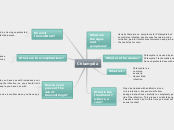
Angelman syndrome (AS)
Is a rare genetic disorder that affects brain development and is characterized by a number of distinctive features and symptoms.
Treatment
AS is present from birth. However, it is not diagnosed until 6 to 12 months of age.
There is no cure as such for AS, but there are treatments to manage each of the symptoms caused by AS.
Fenotype
And in terms of behavioral traits, hyperactivity, laughter for no reason, sleep disorder, among others, can be observed.
Neurological traits include mental retardation and motor developmental delay, seizures, among others.
Physical traits may include scoliosis, microcephaly, light hair, skin and eyes, among others.
It can be classified into three: physical traits, neurological traits and behavioral traits.
Genotype
The vast majority of cases are not inherited, although in certain cases a genetic change responsible for AS may be inherited from one of the parents.
AS occurs on chromosome 15 and there are 4 genetic mechanisms that cause it:
Deletion of the critical region 15q11-13 (60-75%)
UBE3A mutation (10%)
Paternal UPD (2-5%)
Imprinting defect (2-5%)
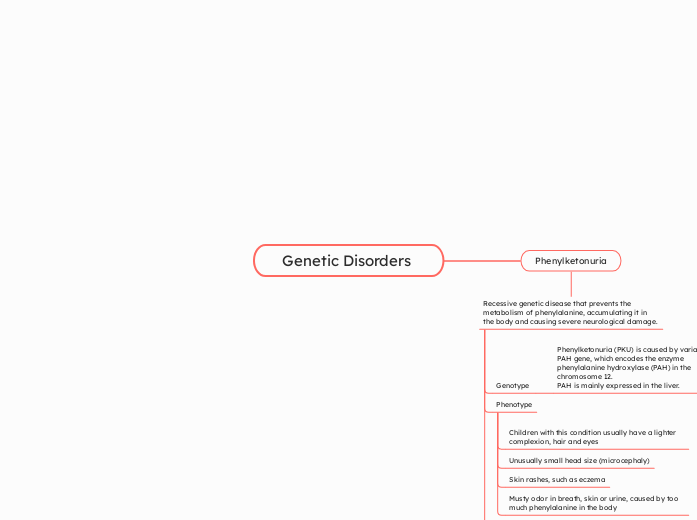
Phenylketonuria
Recessive genetic disease that prevents the metabolism of phenylalanine, accumulating it in the body and causing severe neurological damage.
Treatment
Is controlled with a strict diet, avoiding foods with phenylalanine such as meats, dairy products and products with aspartame.
It is detected in newborns through biochemical tests
Phenotype
Musty odor in breath, skin or urine, caused by too much phenylalanine in the body
Skin rashes, such as eczema
Unusually small head size (microcephaly)
Children with this condition usually have a lighter complexion, hair and eyes
Genotype
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is caused by variants in the PAH gene, which encodes the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) in the chromosome 12.
PAH is mainly expressed in the liver.