B Findings
>30% bone marrow involvement and tryptase >200ng/mL
Dysplasia or proliferation in other lineages, but does not meet definition of another myeloid neoplasm. And with relatively normal blood count.
Hepatomegaly (without liver dysfunction), Splenomegaly (without hypersplenism), lymphadenopathy
C Findings
Mast cell infiltration related cytopenia (Hb < 100, PLT < 100, ANC < 1.0)
Hepatomegaly with impaired liver function, portal hypertension, ascites.
Osteolytic lesions (with or without fractures)
Palpable splenomegaly with hypersplenism
Malabsorption due to GI mast cell infiltrate.
Midotaurin (ORR 60%)
Cladribine (ORR 50%)
?Avapritinib (ORR 77%)
?AlloSCT
- KIT D816V resistant to Imatinib and masatinib
- But for KIT D816V negative patients imatinib can be used
Midostaurin
Avapritinib
Uncertain whether these medication actually change OS. Difficult to determine due to heterogeneity of patients with AHN. It is believed that OS is determined by AHN rather than ASM.
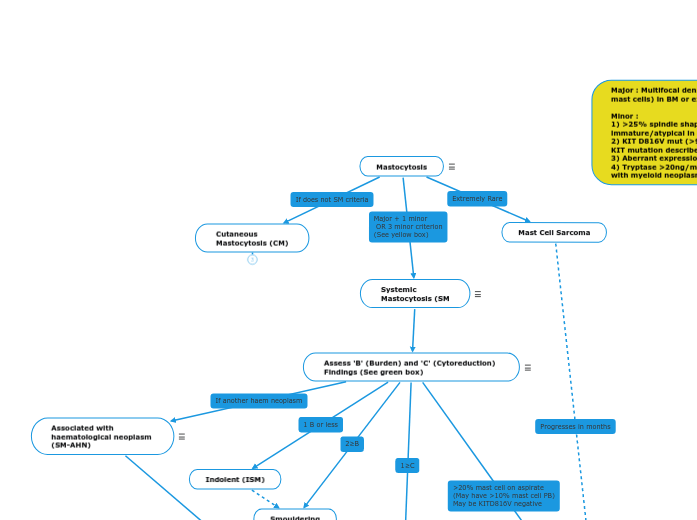
Major : Multifocal dense infiltrate (≥15 mast cells) in BM or extracut. organ
Minor :
1) >25% spindle shape, or >25% immature/atypical in BM
2) KIT D816V mut (>90% +ve, nb other KIT mutation described)
3) Aberrant expression CD25 +/- CD2
4) Tryptase >20ng/mL unless associated with myeloid neoplasm.
Mastocytosis
- Mastocytosis is clonal and neoplastic proliferation of mast cells.
- Usually form ‘multifocal compact clusters’ or cohesive aggregates.
- Considered ‘rare’. Can happen at any age, but cutaneous forms more common in children.
- Disease range from dermatological lesions that regress, to life-threatening multi-or
Mast Cell Sarcoma
Systemic
Mastocytosis (SM
- Mast Cell Activation Syndrome : Symptoms compatible with mast cell activation, and significantly raised tryptase.
- MCAS is a significant clinical finding to document.
- If MCAS occur with KITD816V mutation, and SM criteria not met. This becomes monoclonal MCAS.
Assess 'B' (Burden) and 'C' (Cytoreduction) Findings (See green box)
B Findings
- >30% bone marrow involvement and tryptase >200ng/mL
- Dysplasia or proliferation in other lineages, but does not meet definition of another myeloid neoplasm. And with relatively normal blood count.
- Hepatomegaly (without liver dysfunction), Splenomegaly (without hypersplenism), lymphadenopathy
C Findings
- Mast cell infiltration related cytopenia (Hb < 100, PLT < 100, ANC < 1.0)
- Hepatomegaly with impaired liver function, portal hypertension, ascites.
- Osteolytic lesions (with or without fractures)
- Palpable splenomegaly with hypersplenism
- Malabsorption due to GI mast cell infiltrate.
Associated with
haematological neoplasm
(SM-AHN)
- CMML most common, but can be MDS, MPN, MDS/MPN, AML
- Lymphoma and myeloma rare.
- KITD816V common, and can be detected in the non-mast cell neoplasm as well.
Mast Cell
Leukaemia (MCL)
- Poor prognosis. <1 year survival usually.
Aggressive (ASM)
- Destructive nature of mastocytosis is often due to the mediates (histamine, proteases etc) than actual mast cell infiltrate.
- Severe symptoms with elevated tryptase can be called Mast Cell activation syndrome. Although other causes of MCAS exist.
Smouldering
Indolent (ISM)
Cutaneous
Mastocytosis (CM)
Mastocytoma
of the skin
Diffuse cut.
mastocyosis
Urticaria
Pigmentosa