"Teaching methods that emphasize
apprenticeship are designed to give students the opportunity to observe, engage in, and discover expert strategic knowledge in context".
"Domain knowledge alone provides insuficient clues for many students about how to solve problems and accomplish tasks in a domain".
Therefore, even though exploration of the problem and solution spaces might initially lead to incorrect solutions, the teacher can consolidate and build on such an exploration to teach the targeted concepts
Research suggest that withholding support up front and providing it only after learners have failed to perform a task is very effective.
In conclusion, relates to specific problems that arise as the student attemps to acomplish a task
To sum up, inquiry teaching is a strategy of questioning students to lead them to articulate and reine their understanding
To sum up, some form of “abstracted replay,” in which the critical features of expert and student performance are highlighted, is desirable.
Results suggest that delaying expert modeling of a task its particulary effective.
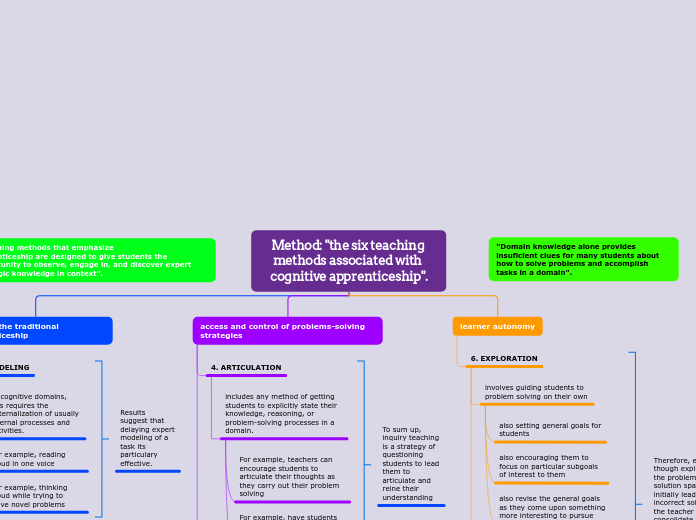
Method: "the six teaching methods associated with cognitive apprenticeship".
learner autonomy
6. EXPLORATION
Furthermore
a teacher might ask students to design solutions to complex problems that target concepts they have not learned yet
the teacher might send the students to the library to investigate and write
involves guiding students to problem solving on their own
also revise the general goals as they come upon something more interesting to pursue
also encouraging them to focus on particular subgoals of interest to them
also setting general goals for
students
access and control of problems-solving strategies
5. REFLECTION
involves comparison's techniques
Replaying the performances to others for
Problem solving
writing
Reading
involves enabling students to compare their own problem-solving
processes
with a model of expertise
with another student
with an expert
4. ARTICULATION
includes any method of getting students to explicitly state their knowledge, reasoning, or problem-solving processes in a domain.
For example, have students assume the critic or monitor
role in cooperative activities in order to articulate their ideas to other students
For example, teachers can encourage students to articulate their thoughts as they carry out their problem solving
Core of the traditional apprenticeship
3. SCAFFOLDING
For example, physical supports.
For example, reciprocal teaching
refers to the supports the teacher provides to help student carry out a task
The supports are transient and only after the student is at an impase
2. COACHING
In students while they formulate questions of the text
Make predictions
Generate summary
Clarify difficulties
Consist of observing students while they carry out task aimed to bringing their performance closer to expert performance.
1. MODELING
For example, thinking aloud while trying to solve novel problems
For example, reading aloud in one voice
In cognitive domains, this requires the externalization of usually internal processes and activities.