jonka Celeste Tiziani 3 vuotta sitten
210
Plan a course
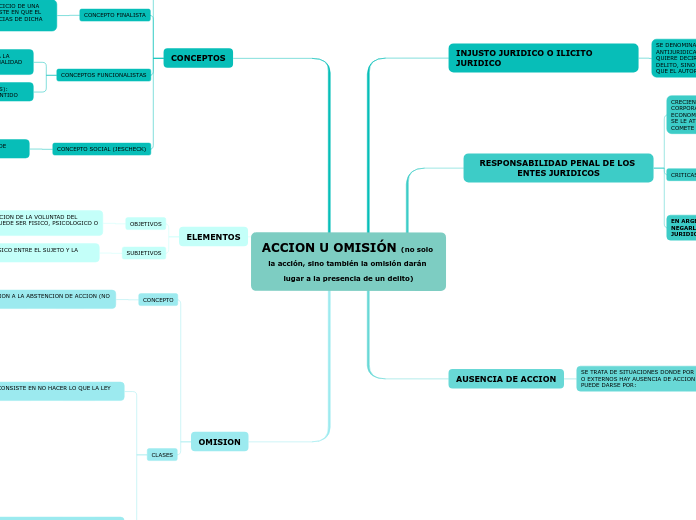
El texto aborda la responsabilidad penal tanto de individuos como de entes jurídicos, destacando cómo la omisión, al igual que la acción, puede resultar en la comisión de un delito.
jonka Celeste Tiziani 3 vuotta sitten
210

Lisää tämän kaltaisia
PECULIARIDADES DEL TIPO OBJETIVO: MUESTRA LA MISMA ESTRUCTURA QUE LA OMISION PURA
AUSENCIA DE LA ACCION: SE NECESITA CONCURRENCIA DE LA POSICION DE GARANTE
SITUACION TIPICA: SE DA CUANDO AL SUJETO LE CORRESPONDEN DOS FUNCIONES
FUNCION DE CONTROL DE UNA FUENTE DE PELIGRO (SE DA CUANDO EL BIEN JURIDICO CORRE PELIGRO EN MANOS DEL SUJETO AL QUE DEPENDE)
PROTECCION DE UN BIEN JURIDICO (SITUACIONES EN LAS QUE SE SOMETE A UN BIEN JURIDICO A DEPENDENCIA DE OTRO)
TIPOS
PECULIARIDADES DEL TIPO OBJETIVO: CONSTA DE TRES ELEMENTOS QUE SON LOS SIGUIENTES
CAPACIDAD DE REALIZAR LA ACCION
AUSENCIA DE UNA ACCION DETERMINADA
SITUACION TIPICA
PECULIARIDADES DEL TIPO SUBJETIVO: SE PLANTEA SI EL DOLO PUEDE REVESTIR LA ESTRUCTURA DEL DELITO, CONFORME A ESTO SE PLANTEAN TRES POSTURAS
SE SUSTITUYE EL DOLO POR EL HECHO DE QUE EL AUTOR NO HAYA QUERIDO REALIZAR DETERMINADA CONDUCTA
SE ADAPTA EL DOLO A LA ESTRUCTURA DE PASIVIDAD
SE NIEGA LA PRESENCIA DE DOLO
Select methods and tools according to
Don't forget to take into consideration if these methods can help you achieve the course goal too.
How do you plan to apply your style to suit the course goals, the size of the class, and the students?
The evaluation must go hand-in-hand with course goals in order to achieve them and also help students to improve their skills.
Also, assignments and homework need to reflect and help achieve course goals.
EN UNA ACTIVIDAD FRENTE A UNA DETERMINADA EXPECTATIVA DE ACCION
EN LA CAUSACION DE CONSECUENCIAS DOMINABLES POR EL AUTOR
...EN EL EJERCICIO DE UNA ACTIVIDAD FINALISTA
These can be partial - short evaluations after each segment of the course - or final - a final exam which will assess all the knowledge aquired during the school year at once.
abarca dos etapas
REALIZACION EXTERNA (EL AUTOR PONE EN MOVIMIENTO LA ACCION)
ESFERA DEL PENSAMIENTO (COMPRENDE EL FIN DE AUTOR)
Decide if you want the assignments completed during the year to represent 1/3 of the final grade.
NORMATIVISMO NEOCANTIANO
POSITIVISMO JURIDICO
Arrange the topics in a logical order.
Discuss how and why you have organized the material in a particular way.
This will help students to see the connections between topics.
ESTADO DE COMA
DESMAYO
EPILEPSIA
SONAMBULISMO
SUEÑO
EMBRIAGUEZ
Select the major topics and determine the order in which you will teach them.
Select the main topics to be covered. To obtain an initial list of course topics, search in current textbooks or in the current literature.
Determine the goals of the course.
Having these course goals in mind will then help you make decisions about which content to include and what kind of assignments and exams are appropriate.
Consider the following questions:
FORMA PERSONAL (LO QUE EL AUTOR QUISO HACER IMPORTA TANTO COMO LO QUE HIZO)
FORMA CAUSAL (IMPORTA LO QUE EL AUTOR HIZO Y NO LO QUE QUISO HACER)