PSYC
Chapter 3
erickson psychosocial development
Psychosocial dilemma: conflict we face b/w personal impulses and the social world
Stage 3: 3-5 -initiative vs guilt:
Stage 2: age 1-3- autonomy vs shame & doubt: encoraging the child to try new skills Autonomy. if they fail and the parents scrold them they will develop shame and doubt in what they do.
Stage 1: Trust vs Mistrust: trust when a child is loved and supported, mistrust when parent is cold and inadequate care
Theory of moral development
kohlberg identified three levels of moral development based on the reasons why the subject came to his/her decision
post conventional: moral behavior directed by self chosen ethical principles that tend to be general, comprehensive or universal
conventional: reasoning based on desire to please others or to follow accepted authority, rules and vaules
preconventional: moral thinking guided by consequence of action (punishment, reward, favors
hereditery/ enviorment
enviorment= nurture
- prenatal envoirment such as a stressed mother, poor health, exposure to x-ray can all lead to congenital problem. teratogens are anything capable of disturbing normal development in the womb
- sensitive period: early experinces can have lasting effects, during this period children are more susceptible to particual enviorments
herdity= nature
- readiness: milestones tend to be governed by a childs readiness for rapid learning. a minimum lever of maturation must occur before another skill is learned. don't start to early or to late.
Chapter 2
handedness
the prefrence for right or left hand, can be inherited, does not necessarily prove that the person is lft/right hemisphere dominant
Cerebral Hemisphere and Lobes
Lobes
temporal- primary auditory area, and language
cerebellum- posture, coordination, muscle tone, memory skills and habits.
occipital- vision
Parietal- sensations like touch, temp, and pressur,
frontal- sense of self, control movement (primamry motorcortex), reasoning and planning
one way to test the halves of the brain individually is to work with people who have split brain.
right hemisphere- perceptual skills. speachless but is able to understand language (jokes, irony, sarcasm), patterns, melodies, express and detect emotion, drawing a picture.
Left hemispheres- analysis.. language, math, time and rythm, coordinating the order of complex movement
The cortex is devided into two hemispheres and is connected by the corpus callusom. The left controls the right side of your body and vice versa.
parts of the nervous system
Spinal cord
the spine can do simple computing on it's own- reflex arc steping on a needle which cause you to reflexively withdraw your foot. damage to the CNS is usually perminent but scientist have been working on CNS repair and have had a few sucesses
peripheral nevous system- intricate network of nerves. nerves vs neurons- nerves are large and have many neuron axons where as neurons are small and have one axon
autonomic
sympathetic
fight or flight system
parasypathtic
return the body to homostasis
internal organs and glandes, involuntary
somatic
voluntary, carries messages to and from organs and skeletal muscles
nerves in the PNS can regrow. They are covered by a thin layer of cells called the neurilemma. this forms a tunnel where damage fibers can follow as they repair themselves. This is why pacients can regain some control after reattaching a severed limb
central nervous system- consists of the brain and nervous system. brain comunicated to the body through the spinal cord. from there the message flows through the peripheral nervous system
Neural Networks
Neuroplasticity
the capacity for our brains to change in response to the enviorment. new synapsis may grow b/w neurons or synaptic conections may get stronger
neural network is an interlinked collection of neurons. 5 neuron synapse with a single neuron connects to three more neurons.
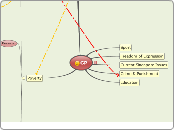
Chapter 1
experimental methods
variables, experiment control, cause & effect, meta-analysis
non-Experimental methods
Naturalistic Observations
survey method
clinical method
correlational study
Three contemporary prespectives
Sociocultural perspective
Stresses the impact that social and contral context has on our behavior.
The whole human
a single perspective is unlikely to fully explain complex human behavior. Perspectives are eclectic and draw insights from other perspective.
A broder view of diversity
Age, ethnicity, gender, religion, disabilityand sexual orientation all affects the social norm that guide behavior
Cultural relavitity
the idea that behavior must be judged relative to the vaules of the culture in which it occurs.
eg. Linda a Native American says there are spirits in the trees near her house. Is she dilusional? No, one must take into account her cultural beleifs.
Psychological perspective
view behavior as the result of psychological process within each person. Emphasize on objective observation, but also congnitive psychology which seeks to explain how mental process affect our thoughts, actions and feelings
Biological perspective
Seeks to explain behaviour in terms of bilogical principles such as brain process, evolution, and genetics. biopsycologist are producting insights on how the brain related to thinkinf , feeling, preception, abnormal behavior, etc.
Pseudopsychology
appeear to be scietific but are false. types of superstitions, beliefs without evidence or in the face of falsifying evidence
BARNUM Effect- a tendency to consider personal descriptions accurate if they are stated in general terms
confirmation bias- personalit traits will contain both sides of a personality for example you are an introvert but sometimes a extrovert. when reading this we remember the stuff that relate to us and prove true, but forget the rest
uncritical acceptance- the tendency to beleive claims because they seem true or it would be nice if they were true.
examples of pseudopsycology are Phrenology ( personality traits could be indicated by skull shape. Palmistry (palm reading), graphology ( personality based on handwriting)
Goals of Psychology
The specific goal of psychology is to describe, understand, perdict and control behaviour. To answer the question of What is the nature of this behavior, Why does it occur, can we predict when it wil happen, and what conditions affect it
Control- the ability to alter the conditions that affect the behavior
Prediction- the ability to forcast behavior accurately
Understanding- means that you can state the reason behind the behavior.
description- naming or classifiying behavior is based on scientific observations (empirical evidence). Does not answer the why
Psychology- The scientific study of behaviour and the mental process
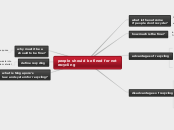
Psychology of Studying- Reflective SQ4R
Review
After reading try to summarize what you have
just read. Restate all the major ieas, relate these
concepts to your own life. This process brings SQ4R
into a full circle as you review all your thoughts and
reading
Reflect
Critical Thinking
Asking questions that require you to
think more deeply about the subject,
and analyse it with more depth. One
way to approch a peice of reading with
skeptism. As you go through the reading
question what is being said which will allow
you to think at a deeper level about what you
are reading
Self Reflection
Connecting new information to information
you already know. eleborate on your
understanding by linking new ideas to your
own experince.
Recite
As you go through your reading
stop and recite back to yourself
what you have just read. This
allows you to process and also
to evaluate what you may have
not understood, giving you a chance
to go back a reread.
Read
ask yourself a question on the topic
before you bein reading. This allows
for more attentive reading and active
learning as you look for the answer to
your question as you read
Survey
an overview of the conecept
before acually reading the topic.
allows for the reader to focus better
on the task at hand