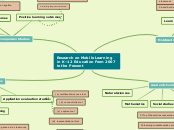
Academic Content
ESL and second-language acquisition
Language arts
Social studies
Mathematics
Natural sciences
Mobilized Learning
M-learning is suggested to provide learners with distinct advantages that can support mobilized curriculum.
Digital inequity
Conflicts with school electronic device use policy
Expanding the school day
Learning outside of classrooms
Noncomparison Studies
Application evaluation studies
Game-based learning
Communication and collaboration
Comparison Studies
Learning objects
Learning context
Neutral learning outcomes
Positive learning outcomes
Five studies explored mobile learning in second-language acquisition
Various approaches to mobile device use for native language learning (mostly in the form of text-based literacy)
Using mobile devices to support social studies education was represented in 11% of the studies
M-learning in mathematics accounted for17% of the research reviewed
27% of the studies researched m-learning within the context of a natural science
access to the mobile device through a school-sponsored program contributed toward socio-educational equity
2.others advocated for using the device as a tool for learning
1.interruptions to the learning ecology
allowing students to
access additional help outside the classroom.
monitor their own progress
work at their own pace
individualize learning
2.hand-held device for accessing information
1.mobile learning in authentic settings outside the classroom
(e) analytical tool
(d) representational tool
(c) capture tool
(b) connectivity tool
(a) multimedia-access tool
The implementation of mobile games in a classroom
The ability to access content and communication with peers and teachers
2.learning object or software
1.mobile device
Five comparative studies found positive learning gains when students learned academic content in a real-world context
2.m-learning had neither a positive nor a negative effect
1.Three studies showed a mixed finding
2.M-learning had greater achievement
1.Nine comparative studies showed a positive learning outcome
Research on Mobile Learning in K–12 Education From 2007 to the Present