Serotonin
STRUCTURE:
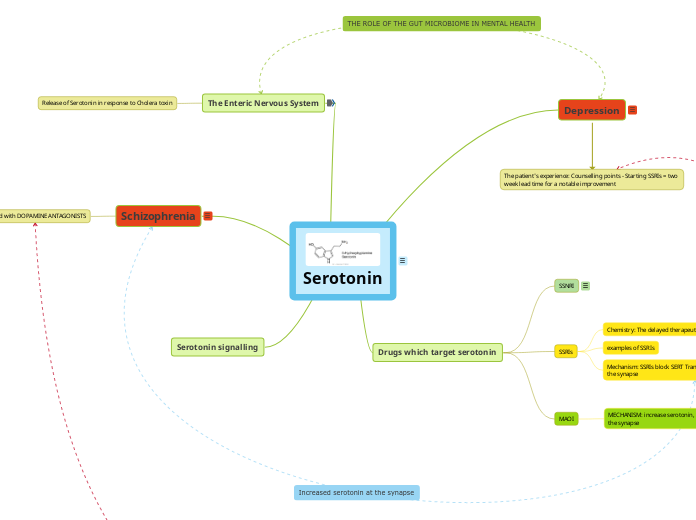
- A monoamine neurotransmitter derived from tryptophan#
- **add structure/ SAR here
FUNCTION:
- play a role in regulation of mood, sleep and cognition and memory
Serotonin signalling
Schizophrenia
PATHYPHYSIOLOGY OF SCHIZOPHRENIA: the serotonin hypothesis
- The DOPAMINE hypothesis
- The SEROTONIN hypothesis
- The GLUTAMATE hypothesis
- The CANNABINOID hypothesis
The Serotonin hypothesis in schizophrenia attributes the negative symptoms of the disease to an overload of serotonin. These increased levels of serotonin reduce dopamine transmission in the forebrain, which is thought to cause negative symptoms.
Atypical neuroleptics target these negative symptoms by blocking this extra serotonin.
Treated with DOPAMINE ANTAGONISTS
The Enteric Nervous System
Release of Serotonin in response to Cholera toxin
Drugs which target serotonin
MAOI
MECHANISM: increase serotonin, but also increase DOPAMINE at the synapse
Parkinson's disease
SSRIs
Mechanism: SSRIs block SERT Transporters to increase serotonin in the synapse
examples of SSRIs
Chemistry: The delayed therapeutic effect
SSNRI
dual selectivity for serotonin/norepinephrine
- duloxetine
- venlafaxine
- milnacipran
Depression
Pathophysiology of Depression- The role of serotonin
The patient's experience: Counselling points - Starting SSRIs = two week lead time for a notable improvement