EL CEREBRO
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
LOBULOS CEREBRALES
TEMPORAL
PARIETAL
OPCIPITAL
FRONTAL
SISTEMA ENDOCRINO
ovarios
testiculos
pancreas
glandulas suprarenales
glandula tiroides
glandula pituitaria
glandula pineal
SISTEMA LIMBICO
es una clase de centro primitivo del cerebro firmemente asociado con la emocion
amigdala
hipocampo
SUBCORTEZA
formación reticular
cerebelo
mesemcefalo
talamo
cuerpo calloso
glandula pituitaria (hipofisis)
hipotalamo
corteza cerebral
SISTEMA NERVIOSO
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
clasificación funcional
sistema nervioso autónomo
mantiene la homeóstasis
sistema nervioso somático
se encarga de la comunicación con el medio ambiente
comunicar tanto del medio ambiente como en el interior de nuestro organizmo
sistema nervioso periferico
Present Perfect Continuous is used:
- to describe an action that started in the past and has continued up to the present
- to describe an action that has just finished
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect Continuous:
- always
- only
- never
- ever
- still
- just
constitución
ganglios
son acúmulos de somas neuronales que están fuera del SNC.
nervios
prolongaciones neuronales envueltas por vainas de tejido conectivo.
autonomo
Structure:
Have/ has + Subject + been Verb-ING?
e.g. How long has he been learning German?
parasimpatico
genera un estado de reposo que permite al organimos ahorrar energia
simpatico
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I have been beingYou have been beingHe/She/It has been beingWe have been beingYou have been beingThey have been being
Form of verb 'to have':
I have been havingYou have been havingHe/She/It has been havingWe have been havingYou have been havingThey have been having
activa las glandulas , incrementa la frecuencia cardiaca
somatico
Structure:
Subject + have/ has been + Verb-ING
e.g. They have been learning French for two years.
Sistema nervioso central
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
PROTECCION
Interrogative form:
Do + Subject (I, You, We, They)+ V1 (First Form of Verb)
Does + Subject (He, She, It)+V1 (First Form of Verb)
Example:
Do I write?
Do you write?
Does he/she/it write?
Do we write?
Do you write?
Do they write?
Type in your own example of a Present Tense verb, interrogative form.
líquido encefalorraquídeo
amortigua golpes, mantiene en equilibrio homeostático los líquidos que bañan al SNC
meninges
estuche oseo
cráneo
columna vertebral
medula espinal
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + do not / don’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
Subject (He, She, It) + does not / doesn’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
e.g. He doesn’t work in a bank.
Type in your own example or choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I am notYou are notHe/She/It is notYou are notWe are notThey are not
Form of word "to have":
I do not haveYou do not haveHe/She/It does not haveWe do not haveYou do not haveThey do not have
cerebro
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.
Examples
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb "to be":
I amYou areHe/she/it isWe areYou areThey are
Form of verb "to have":
I haveYou haveHe/she/it hasWe haveYou haveThey have
COMO SE COMUNICAN LAS NEURONAS
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
neurotrasmisor
Future Continuous is used:
- for an action that is likely to happen in the future and continue for an expected length of time
- for an action that will be in progress at some point in the future
- for action verbs (e.g. running)
- for predictions about future events
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow at 5 o'clock)
gaba
Structure:
Will + Subject + Be +Verb-ING?
e.g. Will you be having fun at the party?
cerotonina
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I will be beingYou will be beingHe/She/It will be beingWe will be beingYou will be beingThey will be being
Form of verb 'to have':
I will be havingYou will be havingHe/She/It will be havingWe will be havingYou will be havingThey will be having
glutamato
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
Will I be being?Will you be being?Will he/she/it be being?Will we be being?Will you be being?Will they be being?
Form of word "to have":
Will I be having?Will you be having?Will he/she/it be having?Will we be having?Will you be having?Will they be having?
norepirefrina
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I will not be beingYou will not be beingHe/She/It will not be beingWe will not be beingYou will not be beingThey will not be being
Form of word "to have":
I will not be havingYou will not be havingHe/She/It will not be havingWe will not be havingYou will not be havingThey will not be having
dopamina
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Be + Verb-ING
e.g. He won’t be having fun at the party.
acetilcolina
Structure:
Subject + Will Be + Verb-ING
e.g. You will be having fun at the party.
En el interior de un axon
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
el extremo derecho del axon esta en reposo , por lo tanto tiene una carga negativa
Future Simple with 'will'' is used:
- to predict the future
- for something with absolute certainty
- when we're talking about a decision at the moment of speaking
- promises, requests, refusals, offers
- future facts
Some adverbs used with Future Simple:
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
SINDROMES
DESCONEXION
Agenesia del cuerpo calloso
puede darse dentro de un contexto malformativo y acompañarse de retraso mental o de manifestaciones psicóticas, aunque también la inteligencia puede ser normal.
Agenesia tardía
se produce a partir del cuarto mes de gestación y es una agenesia de tipo parcial, suelen estar preservados el rostro y rodilla del cuerpo calloso y ausente la mitad posterior, especialmente el esplenio, ya que el desarrollo ontogénico del cuerpo calloso se realza en sentido anteroposterior.
agenesia precoz
se produce antes de las 12 semanas de gestación, en los casos más graves existirá agenesia completa, acompañada de ausencia o malformación de otras estructuras comisurales como el septum o el trígono.
comisurotomía
operaciones que permiten disminuir las crisis epilépticas
Alexitimia
incapacidad o dificultad para la expresión y la interpretación de las emociones.
Anomia olfatoria unilateral derecha
los olores no pueden denominarse cuando son presentados en la ventana derecha de la nariz, sin que se trate de un trastorno anósmico, sino de una incapacidad del hemisferio izquierdo para realizar la denominación del estimulo oloroso, ya que la ausencia de cuerpo calloso impide la trasferencia de información para su tratamiento semántico.
Hemialexia izquierda
consiste en la incapacidad para percibir estímulos con contenido lingüístico presentados por el hemicampo visual izquierdo baja presentación taquistoscópica.
Apraxia constructiva derecha
consiste en la incapacidad para la reproducción grafica de pruebas visoperceptivas.
Apraxia ideomotora unilateral izquierda bajo ordenes verbales
consiste en la incapacidad para ejecutar ordenes verbales y solo atañe al hemisferio izquierdo.
Alexia táctil izquierda
es una derivación de la anomia táctil y se caracteriza por la incapacidad de identificar las letras.
Anomia táctil izquierda
los objetos que no se palpan con la mano izquierda y que no se perciben visualmente.
causado por la perdida de conectividad anatomica y funcional entre ambos hemisferios el cuerpo calloso es la principal estructura de conectividad intermefisferica
cuerpo calloso se distingen 4 zonas
esplenio o rodete
es una zona mas engrosada situada en la parte posterior y conecta entre si los lóbulos temporales y occipitales de ambos hemisferios.
cuerpo o tronco
une aéreas frontales y parietales de ambos hemisferios
rodilla o genu
conecta también ambos lóbulos frontales.
pico o rostrum
situado en la parte anterior, contiene fibras que conectan los ambos lóbulos frontales.
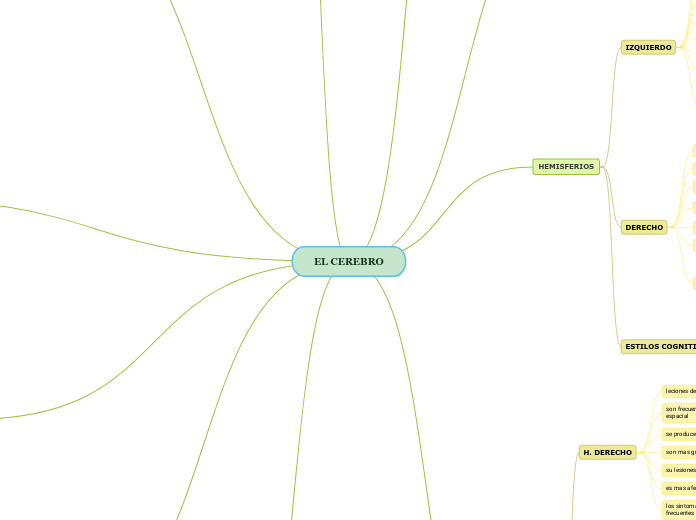
H. IZQUIERDO
el humor tiende al pesimismo y al catastrofismo
su lesiones afectan mas al pensamiento logico conceptual y la capacidad de abstraccion
las apraxias ideatorias e ideomotoras son de mayor gravedad
se producen cuadros afacicos afectando el lenguaje oral escrito
lesiones de menor tamaño
H. DERECHO
los sintomas de euforia y desinhibicion social son mas frecuentes
es mas afectado el pensamiento concreto e intuitivo
su lesiones suelen preservar la estructura simbolica del lenguaje
son mas graves las apraxias constructivas
se producen agnosias de mayor gravedad
son frecuentes los trastornos visoperceptivos y de orientacion espacial
leciones de menor extención
HEMISFERIOS
There are four Past tenses:
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple
- Past Perfect Continuous
ESTILOS COGNITIVOS Y HEMISFERICIDAD
es el estudio de las primeras diferencias cognitivas entre ambos hemisferios
ESTILO HOLISTICO-INTUITIVO-SINTETICO
predominio funcional con el hemisferio derecho los usan las mujeres y los zurdos porque tienden a emplear este tipo de estrategias de tipo bihemisferico.
ESTILO ANALITICO
relacionado con el hemisferio izquierdo su caracteristica usa estrategias de tipo proposicional para la resolucion de problemas( hombres)
DERECHO
Past Perfect Continuous is used:
- for an action that started in the past and continued up to another point in the past
- to show cause and effect
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Continuous:
- since (e.g. since yesterday)
- for (e.g. for 10 years, for 6 months)
se denomina espacial y no verbal
dominante en la expresion de emociones negativas
utiliza un procesamiento aposecional
dominante en el control de la atencion
habilidades espaciales
reconocimiento y expresión de la emoción
reconocimiento de patrones
caras y melodias
visualización
Structure:
Had + Subject + been Verb-ING?
e.g. How long had they been living in London before moving here?
habilidades perceptuales
Structure:
Subject + hadn’t been/had not been + Verb-ING
e.g. I was tired because I hadn't been sleeping.
no verbal
Structure:
Subject + had been + Verb-ING
e.g. They had been talking for over an hour before I arrived.
IZQUIERDO
Past Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that began in the past and is still going on at the moment of speaking
- an action that continued before and after another action
- a change of mind
- an action happening repeatedly in the past
The Past Perfect tense is not normally used alone. It is used to denote the earlier of two past actions. We use Past Simple for the latter action.
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Simple:
- already, before, ever, never
- once, twice, yet
- just, up to then
- for, since
se denomina hemisferio verbal o linguistico
FUNCION
su organización neutral es de tipo focal
dominante para razonamiento matematico
dominante para las expresiones de emociones positivas
ordenar movimientos complejos
ritmo
calcullo
Structure:
Subject + hadn’t (had not) + Past Participle
e.g. They hadn’t met Julia before the party.
escritura
Structure:
Subject + had + Past Participle
e.g. They had already met Julia before the party.
sentido
Structure:
Had + Subject + Past Participle?
e.g. Had they met Sarah before the party?
habla
Past simple expresses:
- an action that happened in the past and has no connection with the present
- an action that happened once in the past
- an action that happened regularly in the past
- an action that was true for some time in the past
- an event or action that already occurred
- an action that is finite - has both a starting and a stopping point
Some adverbs used with Past Simple:
- yesterday
- last month, last year
- ago (e.g. two days ago)
- in (e.g. in 1997)
- never, always, seldom, often, frequently, occasionally, once, twice
lenguaje
Past Continuous is used for:
- an action that happened before another action in the past
- an action that started in the past and continued up to a given time in the past
- an action done several times up to a point in the past and continued to do after that point
- an action that happened in the past but is important at the time of reporting
Some adverbs used with Past Continuous:
- always, only, never, ever, still, just
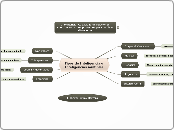
COMO PUEDEN TOMAR DECISIONES LAS REDES NEURONALES
una pequeña red neuronal estelisada
Structure:
Subject + was/ were + Verb-ING
e.g. You were studying when she called.
la neurona A recibe entradas de dos conexiones exitatorias mas debiles y una mas fuerte y dos conexiones imbidoras y combinan las entradas en una desicion para lanzar un potencial de acción
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I was beingYou were beingHe/She/It was beingWe were beingYou were beingThey were being
Form of verb 'to have':
I was havingYou were havingHe/She/It was havingWe were havingYou were havingThey were having
CORTECALIZACIÓN
una corteza mas arrugada tiene mayor capacidad cognitiva, la cortalizacion extensiva es la clave de la inteligencia humana