All of these plants are vascular
Similarities
Both do not have scales and have sensory organs
Have the ability to swim, and breathe using lungs or gills
Characteristics
Both classes of these animals give birth to young and have a layer of heat insulation
Diagram showing types of viruses
Prokaryotes
Diagram
Eukaryotes
Yes
No
Is it Living?
Viruses
Classification of Viruses
Can be classified based on their genetic material
Can be classified based on the size of their caspied
Can be classified based on the shape of their caspid
Structure of a Virus
Has 3 main viral structures
Has an membrane envelopoe after escaping a host cell
Has the Capsid
Has the Nucleic Acid
Why is it non-living?
Can't reproduce without a living host
Has no proper cell structures
Does not react to any stimuli
Are they Eukaryotes or Prokaryotes
Do some of their cells have a cell wall?
Animalia
Do they have a backbone?
Worms
Are usually flat, their body is a tube in a tube, and you can see their head vs their tail
Warm Blooded?
Amphibians
Amphibians have smooth, wetter skin with scales and they are usually slimy
Reptiles
Reptiles are dry, and have scales
Fish
Fish are vertebraes that live in the water, made of cartilage
Have the ability to fly? (The majority)
Birds
A majority of them have the ability to fly aside from a few species
They have feathers to act as their heat insulation
Mammals
They give birth to young, but do not lay eggs
This class of animals have fur for heat insulation
Insects
Their bodies are dividied into segments and their legs have moveable sections connected with joints
Are they motile? (can they move on their own)
Are the MAJORITY of them single celled?
Protists
Types of Protists
This category is for everything that doesn't fit in anything else! (such as Amoeba)
Plant-Like
These protists make their own food using photosynthesis, just like plants do
Fungi-Like
They are decomposers like other fungi, common exmaples include the slime moulds
Animal-Like
These protists consume other organisms as their food source. They also tend to be parasites
Fungi
Classification of Fungi
Fungi imperfecti, Chytrids, Zygospores, Sac fungi, Club fungi
Club fungi have fruiting bodies but are short lived
Sac fungi tend to be the largest fungi we see and have finger-like sacs
Zygospores tend to be multicellular and live on land, an example of this is bread mould
Chytrids are usually unicellular and tend to live in water with special limbs called flagella
Fungi imperfecti are a diverse phyla of fungi
Are the only ones to not reproduce sexually!
How do they get their nutrition?
Parasitic, Predatory, Mutualistic, Saprobial
Others wait for organisms to die, to feast on them
Some partner up with other living things like pants, which is mutually beneficial
Some fungi can hunt/wait for prey
They can be parasites, which means they absorb the nutrients of that come from their host
Plantae
Types of Plants
Gymnosperm
They produce "naked" seeds and have pollen for some animals
Angiosperm
Their plants produce fruit and are known as flowering plants
Pteridophytes
They don't produce seeds and an example of them are ferns
Bryophytes
They do not have vascular tissues, examples are mosses
Is the cell wall made of peptidoglycan?
Bacteria
Cyanobacteria
Is considered bacteria but is extremely close to being considered a plant. It is a prokaryote so it is automatically here.
Classification
Size and Shape, Nutrition, Respiration, Movement
Size and Shape: Archaea and Bacteria can take on different shapes (Spheres, Rods, Spirals)
Respiration: We can describe both archaea and bacteria depending on their respiration type. (Are they Aerobic? Anaerobic? Obligate Aerobes?)
Nutrition: The way they get their food. Some types of archaea are chemoautotrophs, some bacteria are photoautotrophs
The Gram Stain
The Gram stain is something that can be used to ONLY classify bacteria
Bacteria prefer normal conditons to live in, this means they do not like to live in the extremes (extremely cold, hot, salty, etc...)
Bacteria use Photosynthesis as their source of food and this is something that is UNIQUE to them
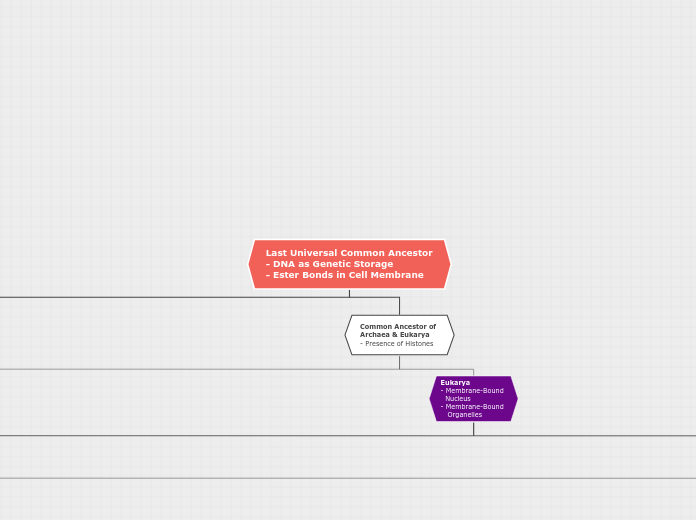
Archaea
Habitats
Halophiles
They can survive in extremely salty conditions
Acidophiles
They can live in extremely acidic conditions
Thermophiles
They can live in extremely hot conditions
Archaea tend to be extremophiles
Nutrition type
Archaea use methanogenesis to produce the majority of their food. A common by-product of this process is methane
The Diversity of Life
Learn more about how a small village on the banks of the Tiber River became the core of one of the most powerful ancient civilizations.