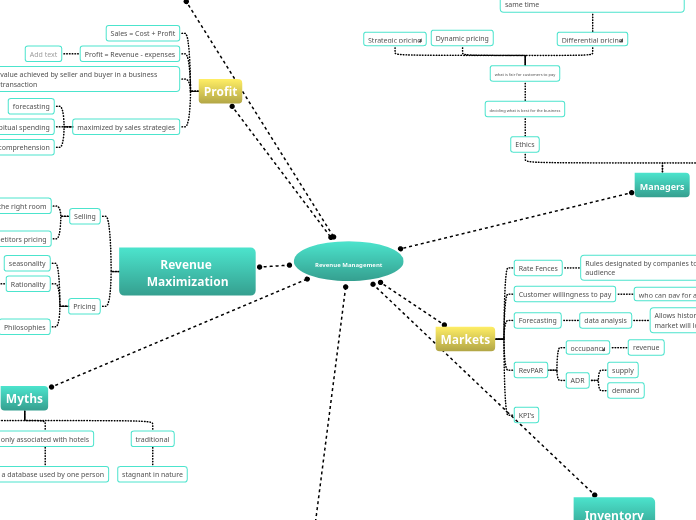
Revenue Management
The 4 (5) C's
*customer
controls all of the above
Cost
amenities contribute to pricing placement
based on buying characteristics
low cost = slack times
logic based
Capacity
Standardization
control over a given service cycle
Clock
time spent using service can dictate price so that revenue is maximized
Calendar
aggrogate demand
Myths
traditional
stagnant in nature
only associated with hotels
only a database used by one person
does not prioritize the customer
Revenue Maximization
Pricing
Philosophies
buyers perspective
sellers perspective
values
Rationality
segmented goals set by business
seasonality
Selling
identifying the competitors pricing
the right room
at the right time
at the right price
through apropriate channels
to maximize company revenue
to the right customer
Profit
maximized by sales strategies
menu comprehension
habitual spending
placing product in the right market
forecasting
value achieved by seller and buyer in a business transaction
Profit = Revenue - expenses
Sales = Cost + Profit
customer-centric
Satisfaction
Memberships
Evaulations
Reviews
Price dictation
fit market
the service/product
the customer
Inventory
yield management
allocation
distribution of inventory allows maximization of revenue
price points
strategic planning
Cost-based pricing
involves summing product costs with desired
profit
Add text
Markets
KPI's
RevPAR
ADR
demand
supply
occupancy
revenue
Forecasting
data analysis
Allows historical data to predict what the future
market will look like
Customer willingness to pay
who can pay for a given product or service?
Rate Fences
Rules designated by companies to reach a desired audience
Managers
Communication
building relationships
amenities
tailored experiences
Short-term connections
Long-term connections
Ethics
deciding what is best for the business
what is fair for customers to pay
Differential pricing
charging a different rate for same service at the same time
arrival time,
Length of use
cancellations
deposits
Dynamic pricing
Strategic pricing