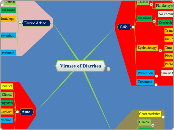
Viruses of Diarrhea
Finish Rotavirus
Astro
Supportive
All age groups
Highest attack rate?
12 hrs - 3 days
Tissue culture
Duration: 3-7 days
Median duration of viral excretion: 20 days
Rotavirus GI-tis
Symptoms indistinguishable from Rotavirus-induced gastroenteritis except disease is milder
7 serotypes
Star-shaped
Enteric Adeno
No specific AV
Hand washing
Vaccine for military
CAVEAT: Only covers serotypes 4, 7, and 21
8-10 days
Longer than most enteric viruses
Children < 2 y.o.
Group with highest incidence
Not detected by routine techniques
Tissue culture is gold standard for adenoviruses, but enteric adenoviruses (serotypes 40 and 41) are not detected by routine tissue culture techniques.
Molecular techniques used by research labs
DNA probe
Commercial kit
Diarrhea: 5-12 days
Vomiting: 2-3 days
Mild respiratory symptoms
Otherwise indistinguishable
Viral GI-tis
2nd most common cause of viral GI-tis in hospitalized patients
Serotypes 40, 41
..cause what illness?
GI-tis
Capsid
12 pentons
antennae projecting from vertices
Linear DS DNA
Rota
Reoviridae
IV/NG feeding
Contact isolation
Hand-washing
Chemical agents
95% EtOH
Chlorinated phenols
Lysol
Vaccine
Rotatrix
Rotateq
Respiratory?
Water-borne
Shedding
Symptomatic, asymptomatic, or both?
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic
Fomites
DCC
DCC = Day Care Center
Nosocomial
Winter
Culture
Expensive
Electron Microscopy
Not readily available
Latex Agglutination / EIA
Cheap
Readily available
Metabolic acidosis
Explosive watery diarrhea
Vomiting
VP4, VP7
Pathophysiology
Replication
Serology
Genetics
Double-shelled capsid
Outer shell necessary for attachment
Segmented genome
11 segments
Hub-wheel shape
Calici
Treatment
Supportive therapy
ORT
Prevention
Epidemiology
Person
Mostly early childhood
Exception?
Norwalk virus: after 1st decade
Place
Time
Seasonality
Incubation period
1-3 days
Syllabus says "10-50 hrs"
Transmission
Fecal-oral
Diagnosis
Research
EM
Electron microscopy
Molecular
Immunoassay
No commercial kit
Clinical
Flu-like symptoms
Abdominal cramps
Myalgia
Anorexia
Malaise
Headache
Fever
Rotavirus symptoms
How does duration and severity differ?
Duration, severity is less
Characteristics
Similar to Rotavirus
Particles released by death of host cell
Viral replication/assembly in cytoplasm
Icosahedral
Genogroups
Hepatitis E virus
Sapporo-like virus
Snow Mountain Like Virus
Norovirus