bio concept map- transport in humans
BLOOD VESSELS
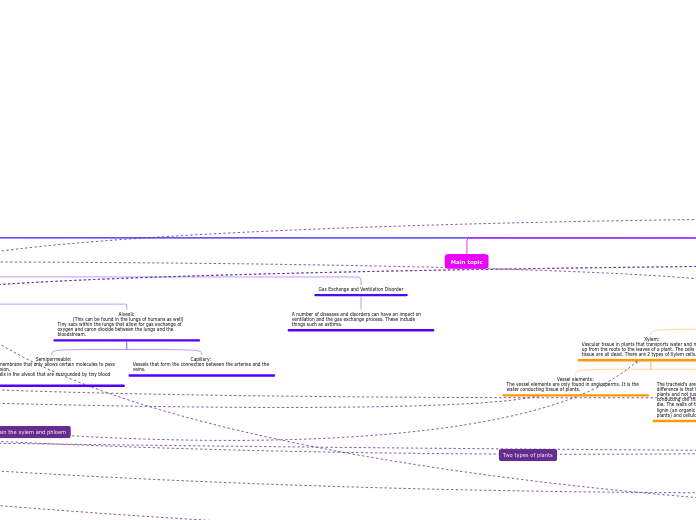
thin walls that are only one cell-thick allow gases to move through to body tissues easily and at a fast rate
the exchange of gases, nutrients and metabolic waste products takes place through capillary walls by diffusion.
Capillaries
Single-layer of cells
Veins
Have valves
ensures blood flows in one direction, preventing backflow of blood
Carries blood from organs to lungs
Carries deoxydenated blood (except pulmonary vein)
Thin walls
stretchable
blood pressure in the veins is much lower than in arteries
Arteries
No valves
Carries blood from heart to organs
Carries oxygenated blood (except pulmonatory artery)
Thick walls
elasticity enables walll to stretch and recoil
to withstand high pressure of blood flowing through from heart
BLOOD
plasma
nutrients, carbon dioxide, waste products (e.g. urea) produced by body cells are transported through the body in the plasma
platelets
Irregularly shaped
cytoplasmic fragments of a large cell (megakaryocyte) produced by the bone marrow
prevent excessive blood loss by causing clotting to occur
white blood cell
phagocyte
produces by bone marrow, lobed nucleus, granular/ non granular cytoplasm, engulfs and digest bacteria in process called phagocytosis
lymphocyte
produced by lymph nodes, round nucleus non granular cytoplasm, produces antibodies during invasion by foreign particles
becomes memory cells that can recognise same invaders
body becomes immune
immune system reacts to the pathogen by producing antibodies against it
administering weekend or deadpathogens to healthy person
agglutination of foreign bodies
attach and bind to the foreign bodies
neutralise toxins
leucocytes
to protect the body against infections and diseases
colourless, irregular in shape, able to squeeze through pores in capillary wall to reach site of infection, has nucleus
red blood cell
acclimatisation occurs when body produces more red blood cells which contains haemoglobin to carry more oxygen so as to compensate for the lower concentration of oxygen breathed into the body with each breath
thin flexible membrane
enable bending through narrow capillaries
no nucleus
increased volume for absorption of oxygen
biconcave shape
increased surface area for absorption of oxygen
has haemoglobin
iron containing protein complex found in red blood cells which has high affinity for oxygen; carries oxygen
HEART
septum
prevent mixing og oxygenatedand deoxygenated blood
left
ventricle
most muscular, excert very high pressure on blood, pump oxygenated blood from heart to all parts of body
receive oxygenated blood from pulmonary vein and pump into left ventrivle
biscupid valves
right
ventricle
less muscular, pump deoxygenated blood to lungs
atrium
receive deoxygenated blood from vena cava and pump into right ventricle
triscupid valves