da athirah ahmad mancano 6 anni
215
chapter 1
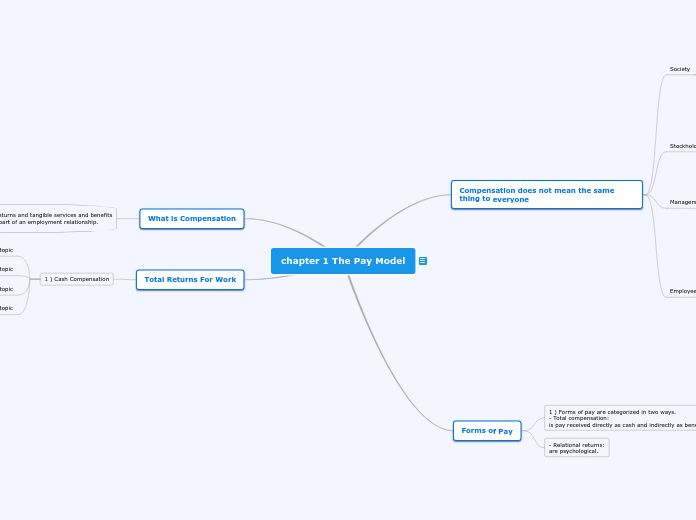
Compensation encompasses all financial returns and tangible benefits employees receive from their employment. It includes direct cash payments and indirect benefits, forming the total compensation package.