diversity map
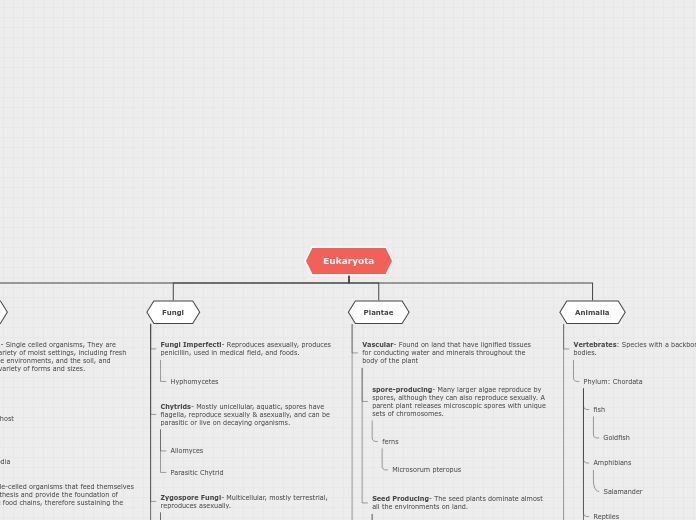
Eukaryote
Plantae
Animalia
Arthropods
Chordates
Vertebrate
Mammals
Primates
Gorillas , chimp
- thumbs
- flexible hip and shoulder
- nails or claws
- can walk on two feet
Rodentia
Hamsters , rats
Two pairs of incisors
Gap between incisors and molars
Complex jaw musculature
Baculum (penis bone)
Carnivorous - eats other animals to survive
Placenta order
humans
nourished placenta
Marsupials
Kangaroo
small immature fetus
Monotreme
duck
egg layers
- has hair
- 4 heart chamber
- lactation (females )
- three middle ear bone
Agnathans
Lampreys (look like leech), Hagfish
(produce slime when irritated)
Notochord persists into the adult animal.
Do not have hinged jaws or bony skeletons.
No paired limbs
Skeleton of cartilage
- turns into adult animal
- no hinged jaw
- no impaired limbs
- skeleton cartilage
Gnathostomata
Reptiles
Turtles
- 3 chambered hearts
- clawed toes
- anomtic egg
Aves
_Feathers
Hollow bones with air sacs
Gizzard
Endothermic (warm blooded)
Amniotic egg
4 chambered heart
Forelimbs are wings
Chicken
Amphibians
Frogs
The amniotic egg
internal fertilization
water tight skin
- young 2 chambered
- adults 3
- gills , lungs , skin for respiration
- live on land and water
- fertilized externally
The body is dived into 3 parts
regions : head , neck , body
- two part appendages ( arms/legs)
-closed circulatory system (blood veins )
- lungs or gills are respiratory
- two layered skin epidermis and dermis (outer and inner )
Cephalochordate
Invertebrates
- filter feeder ( the suck water through their gills and use gills as filters )
Urochordate
- display chordate characteristics
- once settled they place anchor (metamorphosis )
- results in losing chordate characteristics
- Dorsal nerve cord
- develops into nervous tissues (humans)
-supports body
- paired gills slits
-tail runs past anus
Mollusca
Echinoderm
Star fish
Marine living only
5 paert radial symmetry around a cetral disc
no head , but has tube feet
visceral - contains organs
mantle - thin layer of tissue which covers most of the body like a cloak
foot - tentacles for catching prey
shells - made by glands in mantle
body plan : many have protective shells
Gastropods
- Found in marine , Freshwater
-have radula use to scrape land
- others are carnivorous
Bivalves
- 2 part shell held by strong muscles
- no head
- filter food by water passing over gills and sweep into their mouths
Cephalopods
- fast moving
-intelligent
- excellent vision (octopus visual learners )
- only class with closed circulatory system
Annelida (segmented worm)
Coelomate : true fluid filled body
digestive tract
closed circulatory system ( blood lives in vessels )
Nematoda (round worms )
pseudocoelomate: doesnt have true body cavity
bilateral symmetry
digesgetive track ( goes in 1 way comes out other )
like cnidaria
Platyhelminthes (flat worms)
Planaria has a pharynx that collects food
- carnivorous
blood fluke : free living / parasitic
- humans tend to be a host
Acoeclomate: filled with cells
- bilaterally symmetrical
-3 tissue layers (meso,ecto,endoderm )
- no coelom
- no circulatory , or skeleton
- induced planaria (fluke)
Chelicerates
- 2 body segments
- six appendages ( 4 walking , 2 chelicerae and pedipals ) which is mouth
- no mandibles or antenna
Crustaceans
- has mandibles
- compound eyes
-appendages (2 toes )
Myriapods
- has antenna
- myriads of legs
- mandibles (mouth)
Cnidaria
Jellyfish
1st animal to grow sensitive tentacles
- able to feel whats around them
Porifera
sponges
First animals on earth
Anthophyta
Flowering plant:
reproduction is inside of flower
- pollination is method used to carry seeds and gametes (gametes microscopic )
- two cotleydon ( peas)
- produces 2 leaves
- stems get thicker with age
- flowers in 4-5
-lage primary root and small secondary
- only one cotyledon (corn )
- seed germinates only prouduces 1 leaf
- stems are flesh like and un branched
- three parts to flower
- parallel pattern
- roots = small branching
- sepals usally same colour
Cycadophyta
- naked seeds
- not covered with fruit
- sporophyyte produces M and F cones
- four phyla : cycads, conifers , ginkgo
Lycophyta
- club mosses
- vasuclar tissue
- live is moist places
- sperm swims to egg
- leaves referred to as fronds
-sporphyte
Bryophyta
Subtopic
- mosses
- doesn't have vascular tissue
-small
- appear leafy but lack true stems , roots/ leaves
To prevent loss moisture :
- have waxy coat
- guard cells
- contorl exchabge of gases (stomata )
- multi cellular
- cell wall made of cellulose
- Contain chlorophyll a and b
- Alternation of generations
- 1. genrationis gametophytes
- 2. sporophyte ( release spores)
Fungi
Mycota is the imperfect fungi
- E.g Hyphomycetes
Hyphomycetes
Basidiomycota is a "club fungi "
- E.g Mushrooms
Mushrooms
Ascomycota are sac funges
- E.g , yeast , truffles
yeast sac fungus
Zygomycota is common molds
-E.g , Bread mold
black bread mold
Protista
Three Groups
Fungi-like protists:
-cant make their own food
-Majority decompose-rs
- sucks up nutrients form other living
- likes Cool, shady , most places
- leaves trails of slimy substance when they travel
- E.g slime molds
Apicomplex
Plasmodium
Animal like protists AKA Protoza:
- many are diseas causing
- must ingest food . Receives food two different ways 1. Holozoic( eats food through endocytosisi ) , 2. Saprozic( absorb predigest food )
- Reproduces by binary fission
-lives in water
- E.g Amodea
Ciliophora
Paramecium
Plant like protists :
- has Chloroplasts to carry photosynthesis
- Asexual reproduction (binary fission) , sexual conjugation
- Lives in wet , moist environments
- E.g Algae
Rhodophyta
Red algae
- can be unicellular or multi cellular
- heterotrophs and autotrophs
- Reproduces asexually (binary fisson)
little exchange of DNA
- aquatic environments are its home: fresh/ salt water , animal fluids , damp area
-Eukaryotic : has nucleus , vacuoles , and mitochondria
-small able to see under light microscope
-move using pseudos (ameba) , cilia(paramecium) , flagella (euglena)
-
Bacteria
Eubacteria
Shape:
- coccus: round
- Bacillus : Rod
-Sprillum: Spiral
Aggregation:
- Mono: one
-Diplo: two
- Strepto: Chain
-Staphylo: Clump
Gram reaction:
- purple = positive
- red or colorless =negative
S.Minus (sprillum )
Corynebacterium
Streptococcus
- cell wall made up of carbohydrates for protection
-cell membrane
-flagella to get around
- cytoplasm
-unicellular ( consist of single cell)
-prokaryotes
- single chromosomes form small piece of floating DNA called plasmid
Archaeans
- the oldest organism
-can live in earths most harsh environment
-thrives in really hot, acidic and salty conditions
Archaebacteria
Anaerobic methanogens
pyrobolobus
-mainly live in gut of animals
-or bottom of methane
- which is how gas is produced on earth
Thermophilies
- bacteria that can tolerate extreme hot weathers
- these bacteria live naturally forming hot springs
Halophiles
Halo bacterium
- salt loving bacteria
- lives in extreme salt conditons
- dead sea
-