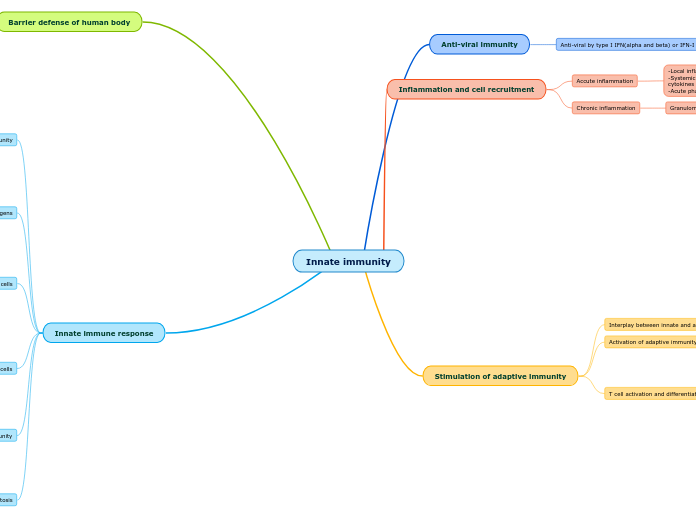
Innate immunity
Innate immune response
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis event
-Chemotaxis and adherence of microbe to phagocyte
-Ingestion of microbe by phagocyte
-Formation of a phagosome
-Fusion of the phagosome with a lysosome to form a phagolysosome
-Digestion of ingested microbe by enzymes
-Formation of residual body containing indigestible material
-Discharge of waste materials
-Professional phagocytes :Neutrophils, Monocytes/Macrophages
-Non-professional phagocytes: Epithelial cells,Fobroblast,Dendritic cells
Humoral substance of innate immunity
Cytokines, mediators, complement system
Peripheral blood immune cells
Monocytes
Basophils
Eosinophils
Dendritic cells : professional APCs
Neutrophils: a professional phagocytic cell
NK cells : distinc from T and B cells in that lacks antigen-specificity and recognize on MHC I
Tissue immune cells
Macrophage
-Professional phagocytosis cells
-Professional APCs
Intraepithelial lymphocyte (IELs)
Recognition of pathogens
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
Type of PRRs
- Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
- NOD-like receptors (NLRs)
- RIG-like receptors (RLRs)
- C-type lectin receptors (CLRs)
Stimuli
DAMPs : derived from host cell
PAMPs : derived from components of microorganism
Characteristic of innate immunity
No memory
Non-specific responses
Rapid/quick response
Stimulation of adaptive immunity
T cell activation and differentiation
Th2
-antibody-mediated immunity
-extracellular parasites
-asthma, allergy
Th1
-cell-mediated immunity and inflammation
-intracellular pathogens
-autoimmunity
-inflammation
Activation of adaptive immunity
Interplay between innate and adaptive immunity
Inflammation and cell recruitment
Chronic inflammation
Granulomatous inflammation
Accute inflammation
-Local inflammatory response
-Systemic inflammatory response : Interaction of various cytokines
-Acute phase protein: C-reactive protein
Anti-viral immunity
Anti-viral by type I IFN(alpha and beta) or IFN-I
Barrier defense of human body
Biological barriers : normal flora
Chemical barriers : lysozyme, low stomach pH,
mucous membranes, anti-microbial peptides
Mechanical/Physical barrier : skin,ciliary clearance