Aplicando estos tres temas principales
Podemos desarrollar
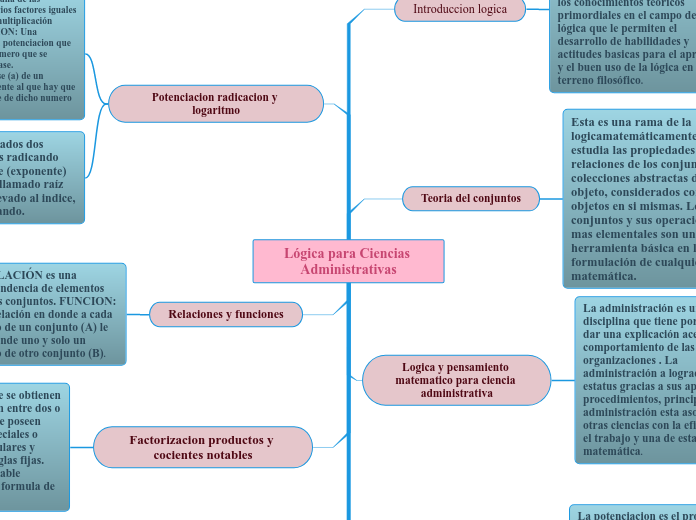
Logaritmo
Exponente al que hay que elevar un número, llamado base, para obtener otro número determinado.
Propiedades
Logaritmo de una raíz
Logaritmo de una potencia
Dividion de igual base
Multiplicación de igual base
Logaritmo de unidad
Logaritmo de base
Logaritmo Natural o Neperiano
Base N° e
Logaritmo Decimal
Base 10
Permutación, Variación y Combinatoria
Importa el orden
Combinación
Combinación con repetición
Si
Participan todos los elementos
Permutacion
Permutacion con repeticion
Se repiten los elementos
No
Variación
Variacion con repeticion
Binomio de Newton
Convierte un binomio a cualquier potencia de exponente N
Observación
La suma de los exponentes en cada término es igual al exponente de (a+b) elevado a la n
Los exponentes de a disminuyen en 1 y los de b aumentan en 1
Inducción
Razonamiento que permite demostrar proposiciones que dependen de una variable n que toma una infinidad de valores enteros
La demostración está basada en el axioma denominado Principio de la inducción matemática.
Racionalización
Racionaliza los denominadores
Eliminar radicales del denominador
Suma o diferencia de un número real y un cuadratico
Suma o diferencia de raices cuadradas
Radical
Elimina las raíces del denominador
Operaciones con radicales
Distinto índice
Igual índice
Adicion y Sustraccion
Radicales no semejantes
Radicales semejantes
Notación científica
Nos permite expresar distintas cantidades con mayor facilidad en forma de potencia
Radicación
Dados dos números: Radicando e Índice, se halla un tercero llamado: Raíz
Raíz de un cociente de igual o distinto índice
Raíz de una raíz
Raíz de un producto de igual o distinto índice
Potenciación
Multiplico por si misma la base, tantas veces como indique el exponente.
Características
División de potencia de igual base o de igual exponente
Potencia de otra potencia
Producto de potencia de igual base o de igual exponente
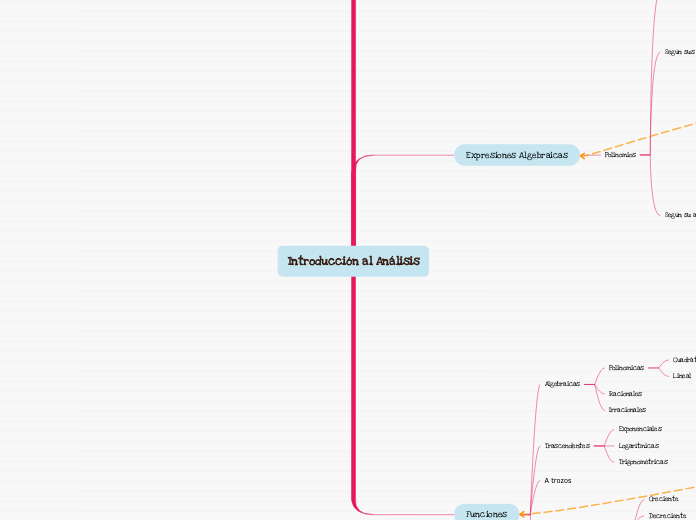
Introducción al Análisis
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
Funciones
The ending of a story is essential. We all know that if the ending is weak, what happened before loses its importance. So make it unpredictable, but fair. A resolved ending answers all the questions and ties up any loose threads from the plot.
Análisis
Analítico
Conjunto de Ceros
Máximo y Mínimo
Conjunto de Negatividad y Positividad
Intervalo de Crecimiento y Decrecimiento
Dominio e Imagen
Biyectiva
Suryectiva
Inyectiva
Gráfico
Discontinua
Continua
Decreciente
Creciente
A trozos
Trascendentes
This is the closure section of the story.
See examples of possible outcomes below:
- all problems have been solved
- it's clear how each one of your characters ends up
- your main character is transformed by the challenge
Trigonométricas
Try answering these questions in order for you to come up with a closure:
- Have all problems been solved?
- Is it clear what happens with all your characters in the story?
- Has the challenged transformed your main character?
- How do the characters feel in the end?
Logarítmicas
Exponenciales
Try answering these questions to come up with a closure:
- Have all the problems been solved?
- Is there a clear picture of what happens with each character in the story?
- Has the challenge transformed your main character?
- How do the characters feel in the end?
Algebraicas
This is the moment when the main character surpasses the last obstacle and finally faces their greatest challenge.
The climax usually follows one of these patterns:
- realization
- resolution
- choice
Type in your answer.
Irracionales
Racionales
Polinomicas
Lineal
Cuadrática
Expresiones Algebraicas
The middle of the story is where you add layers of complications that will lead to the end. Reveal more about the character's journey. Did their personality go through changes? How did they overcome the challenges? And as you build up the story’s central conflict, make it more personal to that character. Also, from the middle act, you have to lead into the final act.
Polinomios
Each story has a main character and that character usually needs to solve a problem or challenge. The character's challenge is the one that creates tension throughout the story.
Según su análisis
Type in any other challenges which other characters in the story need to face.
Podemos aplicar
Valor numérico
Coeficiente principal
Termino principal
Grado
Operaciones
División
Multiplicación
Resta
Suma
Factoreo
Regla de rufini
Teorema del resto
Teorema de gauss
Diferencia de cuadrado
Cuatrinomio cubo perfecto
Trinomio cuadrado perfecto
Factor común en grupo
Factor común
Según sus términos
Cuatrinomio
Trinomio
Binomio
Monomio
Según sus grados
In most stories, there are 3 challenges. The number 3 is a mystical number symbolizing completeness. Try to come up with interesting challenges with which your character needs to struggle.
See a few examples below:
- turns into a werewolf at night
- is sent back in time
Polinomio de tercer grado
Polinomio de segundo grado
Polinomio de primer grado
Conjunto Numérico
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
Números Reales (R)
Characters are essential to a good story. Usually, the protagonist(s) is/are the most affected by the plot. Introduce a character by focusing on their actions, interests, and occupation, as the physical appearance doesn't make a difference in most cases.
Números Irracionales (I)
No pueden ser expresados como fracción
Números Racionales (Q)
Type in the name of your character.
Conjunto de números enteros (Z)
Which traits best describe the character's personality? Choose more if necessary:
introvertedloyalkindindependentquick-thinkingadventuresomeidealisticsweet-naturedcalmrisk-takercreativewittystrictfussyweirdclumsyharshaggressivecarelessclingingcowardlycrueldeceitfulimpulsiveOther
Negativos
Ceros
Naturales (N)
Conjunto de fracciones equivalentes
Choose the type of your chacter:
Protagonist (main character)Antagonist (main character's opponent)Flat (stereotypical character)Round (his/ her personality develops throughout the story)Static (doesn't evolve as a person throughout the story)Dynamic (dramatical change in personality)Confidant (the main character trusts him/ her)Foil (contrasting character who enhances the personality of another character)Other
Clasificación
Periódicas Mixtas
Periódicas Puras
Exactas