da Arif Idham mancano 4 anni
332
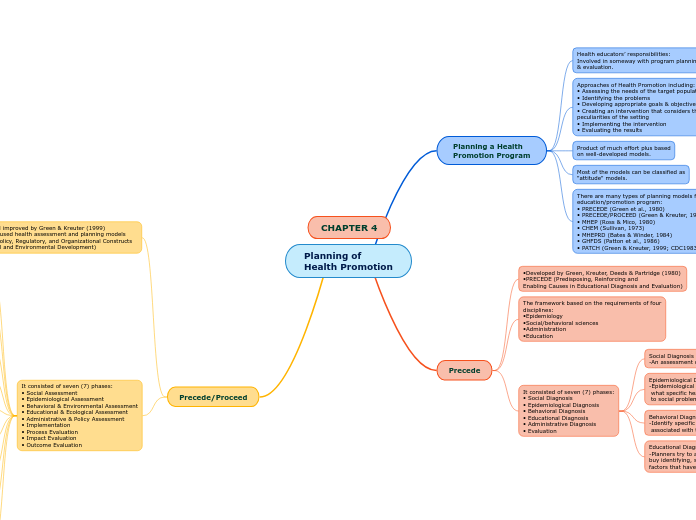
Planning of Health Promotion
da Arif Idham mancano 4 anni
332

Più simili a questo
•Predisposing factors •Enabling factors •Reinforcing factors