da Laura Andra Munar mancano 4 anni
476
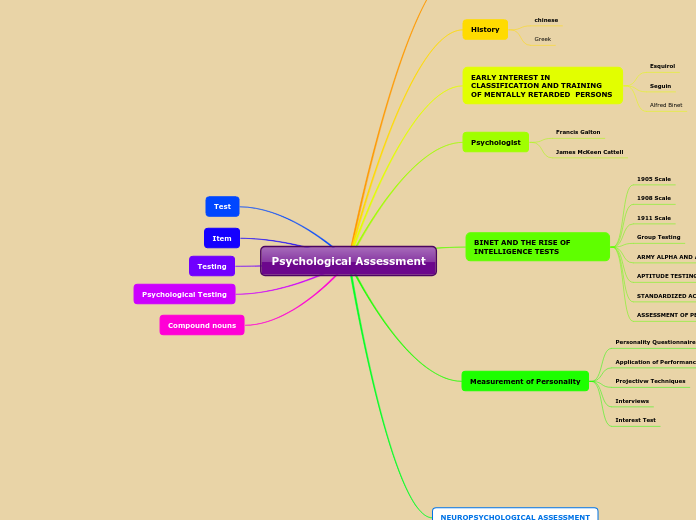
Sample Mind Map
Creating effective educational materials involves developing a principled and flexible framework that aligns with the needs and preferences of learners. It is essential to incorporate the writers'