da Jayde Mahelona mancano 7 anni
408
Unit 4 Respiration
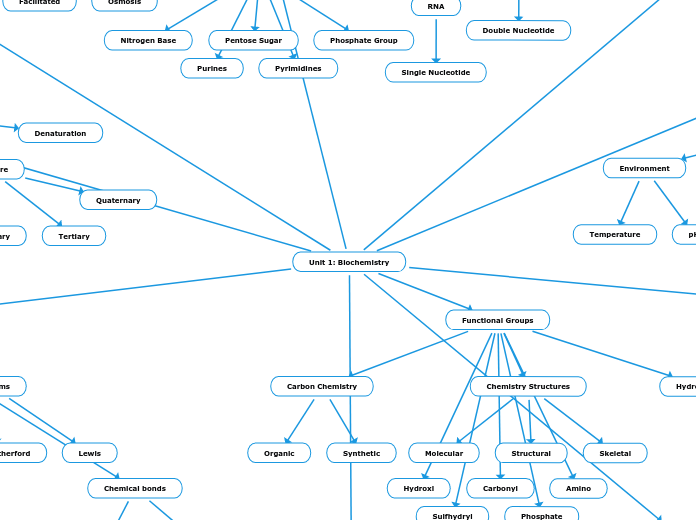
Enzymes are crucial proteins that facilitate various biochemical reactions in the body by lowering the activation energy required for those reactions. They play a significant role in both anabolic and catabolic processes, which involve building up and breaking down molecules, respectively.