da Sricharan K.T manca 1 anno
171
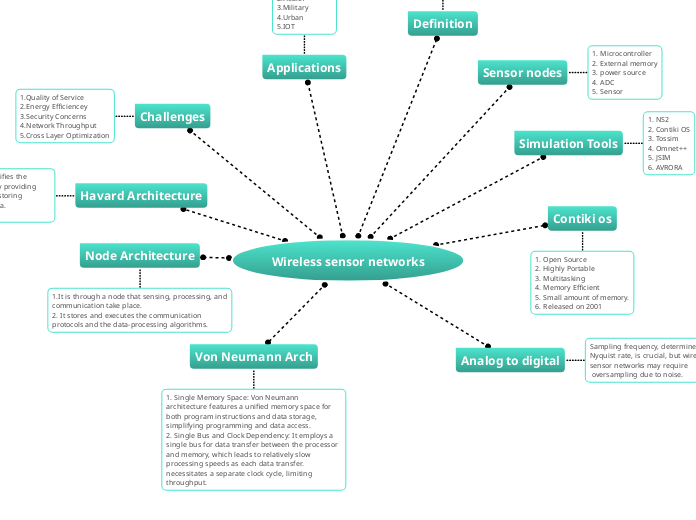
Wireless sensor networks
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) consist of numerous sensor nodes deployed to monitor various environmental conditions. These nodes perform sensing, processing, and communication tasks, adhering to specific architectural designs such as Von Neumann and Harvard architectures.