によって Ahmad E 4年前.
395
Quadratic Equations
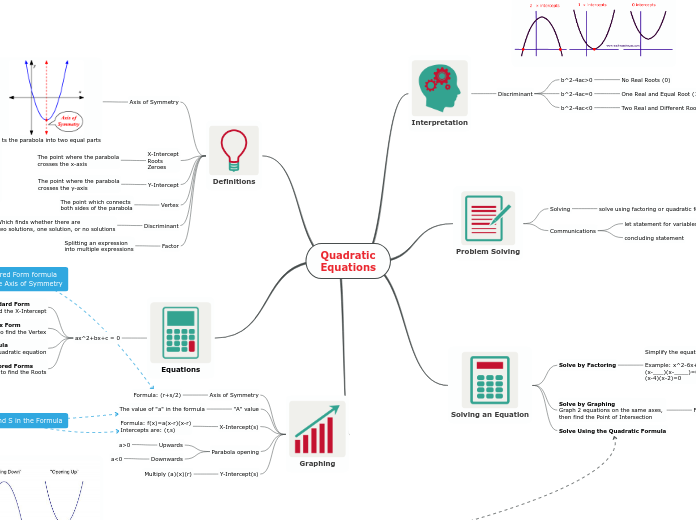
Quadratic equations are fundamental in algebra and involve expressions where the highest exponent of the variable is two. These equations are typically written in the form ax² + bx + c = 0.
によって Ahmad E 4年前.
395

もっと見る
a<0
a>0
f(x) = a(x-r )(x-r )
(-b±√b^2-4ac) / 2a
Vertex y = a(x – h)^2 + k
y=ax^2+bx+c
1) solve for x 2) plug the value of x into the original equation to find y
Zero Product Property When equation has product of two simple equations, one of the two (or both) must be equal to zero
1) Factor 2) Find the 2 Solutions 3) Solve each Equation
Example: (x-4)(x-2) (x-4)=0 because x=4 and/or (x-2)=0 because x=2
Two Real and Different Roots (3)
One Real and Equal Root (1)
No Real Roots (0)