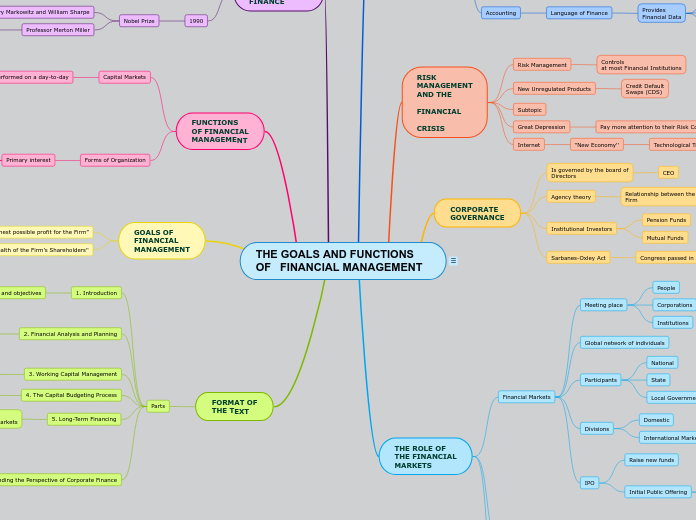
THE GOALS AND FUNCTIONS OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
THE GOALS AND FUNCTIONS OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
FORMAT OF
THE TEXT
Parts
6. Expanding the Perspective of Corporate Finance
Integrative tool
Valuation concepts
Portfolio Considerations
Capital Budgeting
Profit Management
External growth strategy and serves
5. Long-Term Financing
Sources and uses
of funds in the Capital Markets
4. The Capital Budgeting Process
The decision on Capital outlays
Consideration of
Market Value Maximization
3. Working Capital Management
Risk-return Analysis
2. Financial Analysis and Planning
Study
Development of comprehensive pro forma Statements
Budget
construction techniques
Ratio Analysis
1. Introduction
Examines the goals and objectives
GOALS OF
FINANCIAL
MANAGEMENT
''Maximize the Wealth of the Firm’s Shareholders''
“Earn the highest possible profit for the Firm”
FUNCTIONS
OF FINANCIAL
MANAGEMENT
Forms of Organization
Primary interest
Corporation
Legal Entity
unto itself
Most important type of Economic Unit
Partnership
Two or more Owners
Sole Proprietorship
Offers the Advantages
Single-person Ownership
Performed on a day-to-day
Financial Management
Receipt and Disbursement of Funds
Inventory Control
Credit Management
EVOLUTION OF
THE FIELD OF
FINANCE
1990
Nobel Prize
Professor Merton Miller
Area of Capital Structure Theory
Professors Harry Markowitz and William Sharpe
Financial Theories
1950
Finance moved away
Real capital
Long-term Plant and Equipment
Financial Capital
Money
1930
Depression ever
THE ROLE OF
THE FINANCIAL
MARKETS
Capital Markets
Significant impact
Creating tremendous competitive
Securities have a
life of more than one year
Corporate and Government bonds
Preferred stock
Common stock
Money Markets
Short-term securities
Certificates of Deposit
Daily operations
Financial Markets
IPO
Initial Public Offering
Secondary Market
Securities are sold to the public
Primary
Market
Sale of securities
Raise new funds
Divisions
International Markets
Domestic
Participants
Local Governments
Public Financial Markets
State
National
Global network of individuals
Meeting place
Institutions
Corporations
Corporate Financial Markets
People
CORPORATE
GOVERNANCE
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
Congress passed in 2002
Institutional Investors
Mutual Funds
Pension Funds
Agency theory
Relationship between the Owners and the Managers of the Firm
Is governed by the board of
Directors
CEO
RISK
MANAGEMENT
AND THE
FINANCIAL
CRISIS
Internet
“New Economy''
Technological Transformation
Great Depression
Pay more attention to their Risk Controls
Subtopic
New Unregulated Products
Credit Default
Swaps (CDS)
Risk Management
Controls
at most Financial Institutions
THE FIELD OF
FINANCE
Accounting
Language of Finance
Provides
Financial Data
Statement of Cash
Flows
Balance Sheets
Income Statements
Economics
Variables
Taxes
Interest Rates
Inflation
Unemployment
Disposable Income
Industrial
Production
Gross domestic product
Structure for Decision Making
Comparative Return Analysis
Demand Relationships
Pricing Theory
Risk Analysis