by Nicole Fontes 4 years ago
239
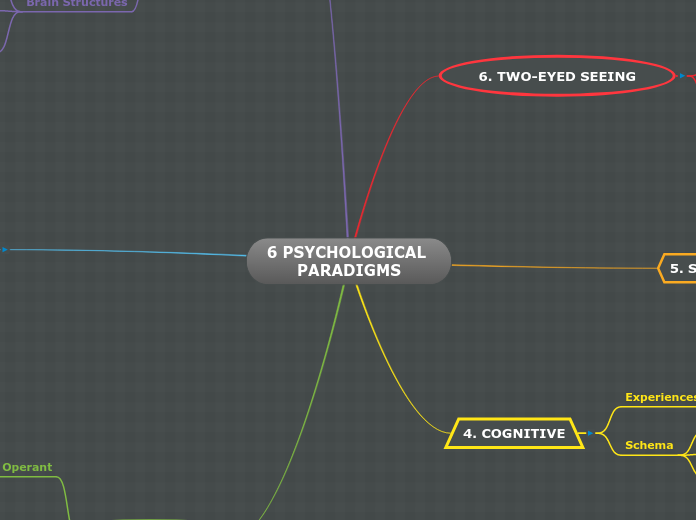
6 PSYCHOLOGICAL PARADIGMS
Various psychological paradigms offer distinct perspectives on human behavior and development. The behavioral paradigm emphasizes the role of environmental stimuli and reinforcement in shaping actions, highlighting operant conditioning and social influences like peer pressure and family role modeling.