by LR - 12NK 902097 Mayfield SS 3 years ago
194
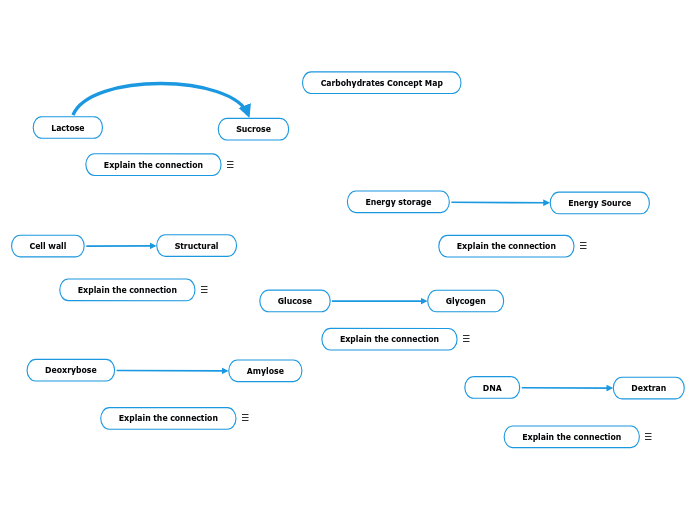
Assignment-Carbohydrates: Concept mapping carbohydrates
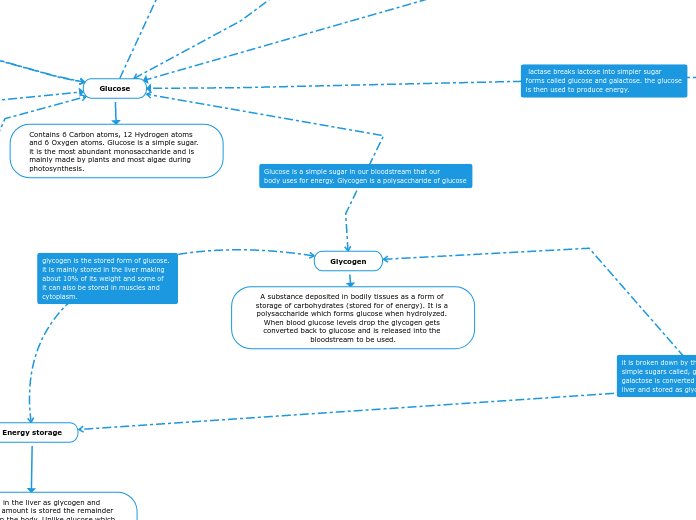
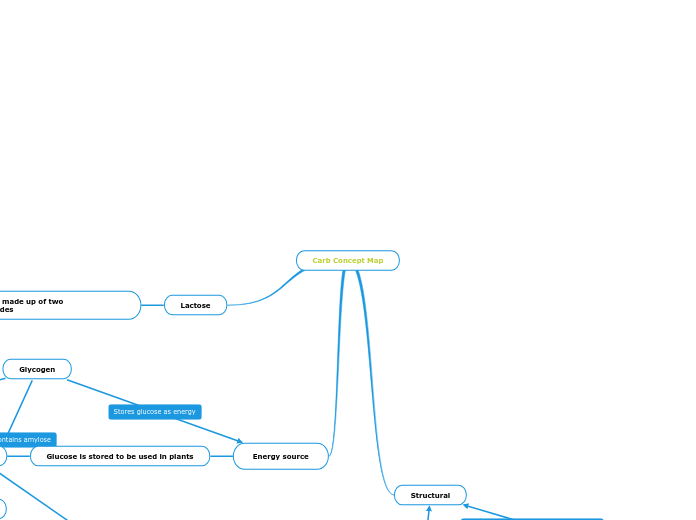
Glycogen serves as a carbohydrate storage in bodily tissues, breaking down into glucose when blood sugar levels drop. Dextran, a branched polysaccharide, forms part of the structural composition in bacteria and yeast.