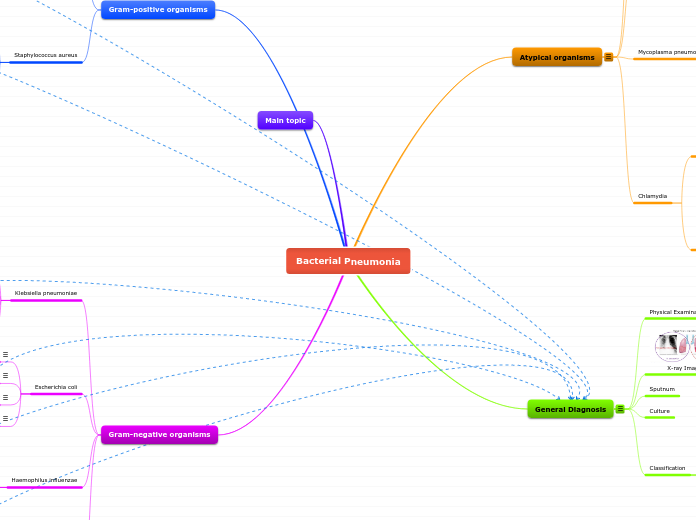
Bacterial Pneumonia
Type in the name of your subject.
General Diagnosis
General:
CBC, Sputum(culture), Radiography(chest), CT scan
Classification
Interstitial
Interstitial Lung Disease
Lobular
Related to inflammation of alveoli
Patchy white, diffuse x-rays; associated with Mycoplasma induced pneumonia
Intra-alveolar space infection; most community acquired pneumonia & bacterial pneumonia
Culture
Sputnum
X-ray Imaging
Bronchopneumonia
patchy white diffuse spots on lung x-ray
Lobar
Opacities in the lungs; may depend on severity of disease; progression of pathology
Physical Examinations
General Signs and Symptoms:
Fever,Rigors, Cough, Runny nose, Dyspnea, Chest pain
Atypical organisms
Atypical in response to antibiotics; Generally stains poorly due to lack of peptidoglycan or irregular cellular wall or absence of one
Chlamydia
Chlamydophila pneumoniae
Virulence Factors 11
Diagnosis 11
Immunofluorescent staining for the presence of the intercellular presence of C. pneumoniae
General Characteristics 11
Non-motile, grown within vesicles, no cell wall, obligate intracellular bacteria
Treatment 11
Azithromycin or Erythromycin for 14 days
Chlamydia psittaci
Treatment 10
Tetracycline or Azithromycin of a week
General Characteristics 10
Non-motile, grown within vesicles, no cell wall, obligate intracellular bacteria
Found in Birds, transmitted via aerosolization of avian feces
Diagnosis 10
serological testing for C. psittaci
Virulence Factors 10
Elementary Bodies, Reticulate Bodies, Inclusion bodies
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Treatment 9
doxycycline, azithromycin, or levlofoxacin
Diagnosis 9
Incubation 3 weeks
Nonspecific flulike symptoms
dry or scantily productive cough
chest x-ray reveals patchy diffuse spots
General Characteristics 9
aerobic,lack cytochromes, enzymes of the citric acid cycle, and cell walls, pleomorphic;
transmitted by respiratory droplets; found in lower respiratory tract
Virulence Factors 9
P1 cytoadhesin,adenosinediphosphate–ribosylase exotoxin
Coxiella burnetti
Treatment 8
Long term antimicrobial treatment (doxycycline); vaccine
Diagnosis 8
Q fever is diagnosed by serological testing
General Characteristics 8
aerobic, obligate intracellular bacteria
transmitted to humans via aerosolized dried feces and urine
Causes Q fever
Virulence Factors 8
C. burnetii infective bodies
Legionella pneumophila
Treatment 7
Macrolides: Erythromycin, azithromycin or clarithromycin
Quinolones: Levofloxacin or gatifloxacin Doxycycline
Diagnosis 7
Abrupt onset of fever, chills, headache and non-productive cough; abnormalities in the GI tract, CNS, liver and kidneys
General Characteristics 7
aerobic, coccobacilli in tissue, filamentous in culture, saprophyte
causes Legionnaire's disease
Virulence Factors 7
proteolytic enzymes, phosphatase, lipase and nuclease, C3b porin binding
Gram-negative organisms
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Treatment 6
combination of aminoglycosides and B-lactam antibiotics
Diagnosis 6
blue-green pigment pyocyanin on agar
General Characteristics 6
Multi-drug resistance; Hospital acquired illness
Gram (-), Aerobic
Virulence Factors 6
adhesins, bacterial neuraminidase, capsule, endotoxin, exotoxin A, exoenzyme S, exoenzyme T, Elastases, Phospholipase C, Antibiotic resistance, Pyocyanin
Haemophilus influenzae
Treatment 5
doxycycline; second generation cephalosporins
Diagnosis 5
Sputum grey or creamy; grows well in C02 enriched incubator on chocolate agar
General Characteristics 5
Gram(-), coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic capnophilic, obligate parasites; normal residents of oral cavity, spread via direct contact, coughing, sneezing
Virulence Factors 5
phagocyte -resistant capsules (PRP), adhesion proteins, lipooligosaccharide, pilus, IgA protease, Outer MB protein
Escherichia coli
Treatment 4
Diagnosis 4
Serological Testing to determine strain
General Characteristics 4
Gram (-), Aerobic or facultative anaerobe, fermentative, catalase (+) rods
Urinary Tract; spread via consumption, commensal organisms, opportunistic infections, soil water, vegetation, -excretion from GI tract, animal reserve
Virulence Factors 4
O antigen, K antigen, H antigen, LPS, Capsule, Antigenic Phase Variation, Exotoxin , fimbriae, intracellular survival and multiplication, siderophores, hemolysins, resistance to serum killing, antimicrobial resistance, verotoxin,
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Treatment 3
Third-generation cephalosporins or fluoroquinolones
Diagnosis 3
Extended Spectrum B-Lactamase Testing
General Characteristics 3
Gram (-), Aerobic or facultative anaerobe, fermentative, catalase (+) rods, capsule;
Nosocomial infections, urinary tract,oropharynx and the GI tract, spread via opportunistic infections,
Virulence Factors 3
Capsule, endotoxins
Main topic
Gram-positive organisms
Add the class information for each week.
Staphylococcus aureus
Treatment 2
floxacillin; Zyvox
Diagnosis 2
Culture Testing; clinical symptoms; golden colonies
General Characteristics 2
Gram (+), catalase (+), coagulase (+), facultative anaerobe, non-motile, cluster of spheres golden colonies
Virulence Factors 2
Capsule, peptidoglycan, lysozyme, protein A, teichoic acids, clumping factor, cytolytic toxins, exfoliative toxin, TSST-1, enterotoxin, coagulate, catalase, haluronidase, fibinolysin, lipase, nuclease, lactamase
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Add class name.
Treatment 1
penicillin; however MDR strains need amoxicillin or erythromycin in extreme cases or allergies
Diagnosis 1
Clinical symptoms; culture confirmation
General Characteristics 1
Gram (+), catalase (-), facultative anaerobe, encapsulated, oval or lancet-shaped, paired or short chains, α-hemolysis
Virulence Factors 1
Capsule, adhesin, secretory IgA protease, pneumolysin, autolysin, hydrogen peroxide
Add additional information about this class.