by Megan Archibald 5 years ago
364
Biotin
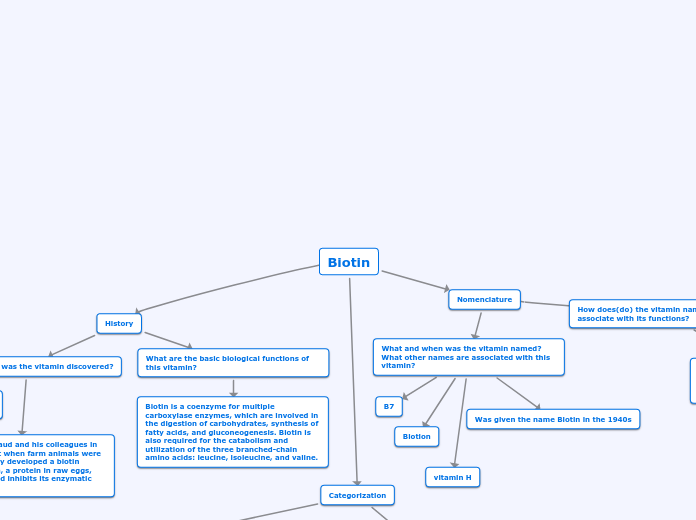
Biotin, commonly known as vitamin H, B7, or B8, is a water-soluble vitamin that forms part of the B-complex group. It plays crucial roles as a coenzyme for various carboxylase enzymes, which are essential in processes like carbohydrate digestion, fatty acid synthesis, and gluconeogenesis.