Biological Molecules
Lipids
Phospholipids
1 phosphate group
2 fatty acids
Triglycerides
1 glycerol
3 fatty acids
Proteins
made from the monomers amino acids
Amino Acids
good pH buffer
Soluble in water
Carbohydrates
Polymers of Sugars
Polysaccharides
Cellulose
Subtopic
Glycogen
An energy store
Highly branched
Starch
Amylopectin
chain
branched
Amylose
helical structure
unbranched
Disaccharides
Lactose
glucose + galactose
Sucrose
glucose + fructose
Maltose
glucose + glucose
Monosaccharides
Hexose (6C)
Glucose
Fructose
Pentose (5C)
Ribose
Triose (3C)
Two membranes
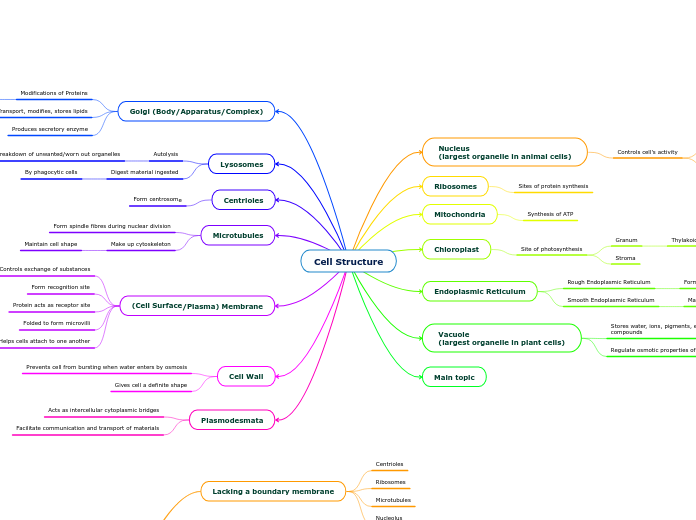
Nucleus
A single membrane
Vacuole
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosome
Lacking a boundary membrane
Cell Structure
A microorganism is an organism so small that people cannot see them with the naked eye.
Microorganisms can be harmful and useful organisms.
Plasmodesmata
Facilitate communication and transport of materials
Acts as intercellular cytoplasmic bridges
Cell Wall
Gives cell a definite shape
Prevents cell from bursting when water enters by osmosis
(Cell Surface/Plasma) Membrane
Helps cells attach to one another
Cell Adhesion
Folded to form microvilli
Protein acts as receptor site
Form recognition site
Controls exchange of substances
Microtubules
Make up cytoskeleton
Maintain cell shape
Form spindle fibres during nuclear division
Centrioles
Form centrosome
Lysosomes
Harmful microorganisms include fungi, bacteria, protozoa, etc.
They cause several diseases in human beings, animals, and plants, which can even lead to death.
The harmful microorganisms not only can damage the human body, but also the food we eat.
Digest material ingested
Give examples of how the spread of harmful organisms can be prevented.
By phagocytic cells
Autolysis
Breakdown of unwanted/worn out organelles
Give examples of how harmful organisms can spread.
Golgi (Body/Apparatus/Complex)
Research about the main characteristics of the microorganisms and give examples!
Produces secretory enzyme
Transport, modifies, stores lipids
Modifications of Proteins
Form glycoproteins
Main topic
Vacuole
(largest organelle in plant cells)
Regulate osmotic properties of cells
Tonoplast
Controls exchange between the vacuole and the cytoplasm
Stores water, ions, pigments, enzymes, sugars, other organic compounds
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Makes lipids & steroids
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Form transport vesicles
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis
Stroma
Granum
Thylakoids
Mitochondria
Microorganisms help in the production of many food items, making medicines, keeping the environment clean, in manufacturing, and in research.
Synthesis of ATP
Give examples of Microorganisms in food production.
Ribosomes
There are five types of microorganisms. Out of these five, four can be free-living or parasitic.
There is one that can be only parasitic since it always reproduces inside other living things.
After enumerating them, click on the flags below to mark the ones which can be free-living and the ones that cannot.
can be free-living
only parasitic
Sites of protein synthesis
Nucleus
(largest organelle in animal cells)
Name the study of microorganisms.
Controls cell's activity
Nucleolus
Makes rRNA & ribosomes
Nucleus Envelope
Allow and control exchange between nucleus and cytoplasm