by Melissa Travis 12 years ago
255
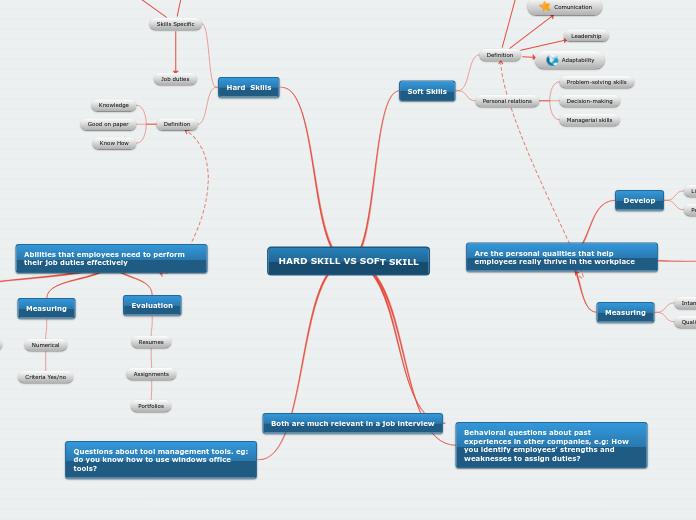
Concept Map of an ID Model
The instructional design approach emphasizes continuous interaction between the instructor and learner, focusing on extracting individual experiences and cognitive processes. This method promotes a holistic consideration of environmental factors affecting learning.