English Curriculum 2020
For Junior High School
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
List of Figures
List of Tables
Table of Contents
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
References
Global Can-do Statements
Basic User II- A2 (Intermediate)
Basic User II (A2)
Can-do descriptors
Adjective / adverb forms
Noun Forms
Verb forms
Clauses
Table 6
9th Grade
8th Grade
7th Grade
Plurilingual and pluricultural competence
Spoken fluency
Pragmatic
Sociolinguistic
Orthographic control
Phonological control
Linguistic
Activities
Written interaction
Spoken interaction
Spoken production
Spoken reception
Format of the grammar component
Figure 2
Examples
Global can-do
statement
Structure
Description of the grammar component
Grammar development
Evolving usage and accuracy
Emerging production
Mostly receptive
Grammatical constructions
Use in terms of pragmatic appropriacy
Meaning
Structure or
form
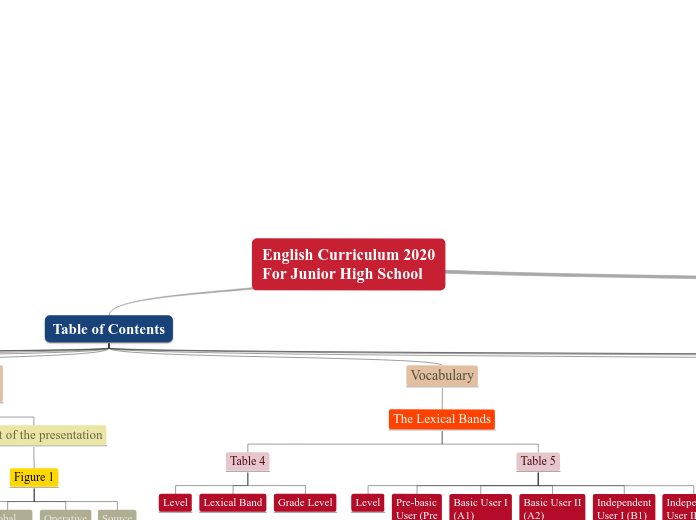
The Lexical Bands
Table 5
Independent
User II (B2)
Independent
User I (B1)
Basic User II
(A2)
Basic User I
(A1)
Pre-basic
User (Pre
A1)
Table 4
Grade Level
Lexical Band
Level
Sources for Can-do Statements and Format of Presentation
Format of the presentation
Figure 1
Source
Operative
can-do
statement
Global
can-do
statement
Activity
Sources
The GEPF
The AUS
The GSE
The CEFR
Levels of Progression
Table 3
Revised English Curriculum 2018
CEFR Global Scale
English Curriculum 2020
Principles to Guide Teaching Practice
Decide on the fourth point of view
Type in the name of the last character whose perspective on the issue you are going to present.
Example: Leslie Burke, Jesse's new next-door neighbor, and best friend.
F. Principles underlying the integration of ICT
E. Principles underlying classroom assessment
D. Principles underlying the design of tasks
C. Principles underlying the selection of materials
B. Principles underlying beginning language learning and teaching
Table 2
A. Principles underlying language learning and language teaching
Point of view
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view. Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: I can't get the poetry of the trees,' he said. She nodded. Don't worry,' she said. You will someday. He believed her.' (Paterson, 4. 24)
Table 1
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Curriculum Components
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
Grammar
Lists of structures
Vocabulary
Words and chuncks
Bands
Domains
Personal domain
Public domain
Occupational domain
Educational domain
Can-do Statements
Operative can-do statements
Global can-do statements
Interdependent dimensions
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
Communicative Competences
Pragmatics
Sociolinguistic competence
Linguistic competence
Phonological and
orthographic control
Grammatical accuracy
Vocabulary size and depth
General
linguistic range
Language activities
What kind of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Mediation
Interaction
Production
Written production
Oral production
Reception
Written reception
Oral reception
Alignment with the
CEFR
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
Introduction
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.