EPUB3 Specification
EPUB Open Container Format (OCF)
application/epub+zip
Resource Obfuscation
ZIP Container
Abstract Container File System
mimetype
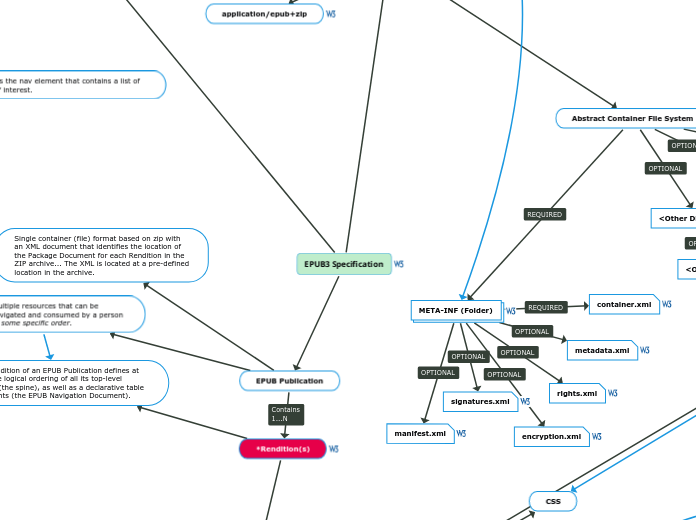
META-INF (Folder)
manifest.xml
rights.xml
metadata.xml
encryption.xml
signatures.xml
container.xml
File Name Restrictions Apply
An OCF ZIP Container MUST meet the conformance constraints defined in OCF ZIP Container.
All OCF Abstract Containers MUST include a directory called META-INF in their Root Directory.
This directory contains the files specified in META-INF Reserved Files. Files other than the ones listed in that section MAY be included in the META-INF directory; OCF Processors MUST NOT fail when encountering such files.
ZIP File Requirements
An OCF Abstract Container MUST meet the conformance constraints defined in OCF Abstract Container.
EPUB Reading System
Use any resources not listed in the Package Document in the processing of the Package.
Ignore proprietary metadata properties that pertain to layout expressions if they conflict behaviorally with the property semantics defined in Fixed-Layout Properties
Process rendering metadata
Process fixed layout metadata, as expressed in Fixed-Layout Properties.
Process the EPUB Navigation Document as described in the conformance section.
Process the Package Document as defined in the conformance section and honor all presentation logic expressed through the Package Documentation
EPUB Publication
Single container (file) format based on zip with an XML document that identifies the location of the Package Document for each Rendition in the ZIP archive... The XML is located at a pre-defined location in the archive.
Consists of multiple resources that can be completely navigated and consumed by a person or program in some specific order.
*Rendition(s)
Each rendition of an EPUB Publication defines at least one logical ordering of all its top-level content (the spine), as well as a declarative table of contents (the EPUB Navigation Document).
*Package Document (package)
last-modified
Together with the package identifier provides a means of distinguishing different versions of an EPUB Publication.
Generic Info
Fixed Layouts
EPUB3 metadata allows for fixed-layout XHTML Content Documents as well as the inherent capabilities for fixed-layouts in SVG.
Allows authors to specify desired orientation, when to create synthetic spreads, and how to position pages within those spreads.
Defines a standard way to represent metadata globally applicable to a collection of pages
Other CONFORMANCE
Is an XML Document & MUST conform to the XML Conformance definition.
Use the file extension .opf
Media Overlay Documents
PLS (Pronunciation Lexicons)
CSS
*Content Documents (a.k.a Publication Resources)
epubReadingSystem (Javascript Object)
RECOGNIZED FEAUTRES
Additional features MAY be added by Reading System developers, but future versions of this specification might append to this list in ways that could conflict or be incompatible with any such custom additions.
spine-scripting
keyboard-events
mouse-events
touch-events
layout-changes
dom-manipulation
METHODS
hasFeature
PARAMS
PROPERTIES
Use of the layoutStyle property is deprecated. Refer to its definition in [ContentDocs301] for usage information.
Returns a String value representing the version of the Reading System (e.g., "1.0", "2.1.1").
Returns a String value representing the name of the Reading System (e.g., "iBooks", "Kindle").
The following properties MUST be made available for retrieving information about the Reading System.
LayoutStyle
version
name
Reading Systems MUST ensure that the epubReadingSystem object is available no later than when the DOMContentLoaded event is triggered [HTML].
Reading Systems MUST expose the epubReadingSystem object on the navigator object of all loaded Scripted Content Documents, including any nested container-constrained scripting contexts.
Pronunciation Lexicon (PLS) Documents
The PLS document filename SHOULD use the file extension .pls.
Document Properties
It MUST be valid to the RELAX NG schema for PLS documents available at the URI https://www.w3.org/TR/2008/REC-pronunciation-lexicon-20081014/ [PRONUNCIATION-LEXICON].
PLS documents MUST be represented and located as defined in EPUB Package — Conformance [Packages32].
PLS documents MUST meet the content conformance criteria defined in PLS Documents — Content Conformance.
The link element hreflang attribute SHOULD be specified on each link, and its value MUST match the language for which the pronunciation lexicon is relevant [PRONUNCIATION-LEXICON] when specified.
PLS documents MUST be associated with the XHTML Content Document to which they apply using the [HTML] link element with its rel attribute set to "pronunciation" and its type attribute set to the media type "application/pls+xml".
PLS Documents MAY be associated with XHTML Content Documents. Each XHTML Content Document MAY contain zero or more PLS document associations.
Fixed Layout Documents
For SVG Fixed-Layout Documents, the ICB dimensions MUST be expressed using the viewBox attribute [SVG].
For XHTML Fixed-Layout Documents, the initial containing block [CSS2] dimensions MUST be expressed in a viewport meta tag using the syntax defined in [CSS-Device-Adapt-1]. In this version of this specification, only the width and height expressions MUST be recognized by Reading Systems.
Reading Systems SHOULD NOT inject additional content such as border, margins, headers or footers into the Viewport.
When rendering Fixed-Layout Documents, the default intent is that the Content Display Area SHOULD occupy as much of the available Viewport area as possible.
It MUST specify its initial containing block [CSS2] as defined in Initial Containing Block Dimensions.
CSS Documents
Text Decoration Level 3
alphabetic
-epub-text-underline-position
left | right
under
-epub-text-emphasis-style
|
||
filled | open
dot | circle | double-circle | triangle | sesame
-epub-text-emphasis-position
&&
right | left
over | under
-epub-text-emphasis-color
Text Level 3
text-transforms
-epub-fullwidth
-epub-word-break
break-all
keep-all
-epub-text-align-last
justify
center
right
left
end
start
-epub-line-break
strict
normal
loose
-epub-hyphens
auto
manual
Writing Modes
-epub-text-combine
-epub-text-combine-horizontal
all
none
-epub-writing-mode
vertical-lr
vertical-rl
horizontal-tb
-epub-text-orientation:
sideways
sideways-right
mixed
upright
It MUST be encoded in UTF-8 or UTF-16 [Unicode].
It MAY include the prefixed properties defined in CSS Style Sheets — Prefixed Properties.
unicode-bidi
direction
SVG Content Documents
It MAY include references to Foreign Resources provided a fallback to a Core Media Type Resource is included.
The SVG Content Document filename SHOULD use the file extension .svg
Restrictions
foreignObject
It MUST be an SVG document fragment [SVG], and conform to all content conformance constraints expressed in Restrictions on SVG.
HTML Deviations & Constraints
Form Submission
Reading System support for the submission of [HTML] forms is OPTIONAL. A Reading System might, for example, prevent form submissions by limiting access to networking.
Embedded SVG
Embedded MathML
ssml
alphabet
ph
prefix
msv
prism
Reserved Options (EPUB-SSV):
aside
figure
list-item
list
table-cell
table-row
table
pagebreak
topic-sentence
keyword
credit
concluding-sentence
noteref
glossref
biblioref
backlink
footnotes
footnote
endnotes
endnote
text-area
sound-area
panel-group
panel
balloon
true-false-problem
question
qna
practices
practice
multiple-choice-problem
match-problem
general-problem
fill-in-the-blank-problem
feedback
assessments
answers
answer
learning-standards
learning-standard
learning-resources
learning-resource
learning-outcomes
learning-outcome
learning-objectives
learning-objective
title
subtitle
ordinal
fulltitle
covertitle
tip
pullquote
notice
case-study
titlepage
seriespage
revision-history
other-credits
imprint
imprimatur
halftitlepage
errata
dedication
copyright-page
contributors
acknowledgments
index-xref-related
index-xref-preferred
index-term-category
index-term-categories
index-term
index-locator-range
index-locator-list
index-locator
index-legend
index-headnotes
index-group
index-entry-list
index-entry
index-editor-note
index
glossterm
glossdef
glossary
tran-info
tran
synonym-group
sense-group
sense-list
phrase-group
phrase-list
phonetic-transcription
part-of-speech-group
part-of-speech-list
part-of-speech
idiom
gram-info
example
etymology
dictionary
dictentry
def
condensed-entry
antonym-group
bibliography
biblioentry
keywords
credits
colophon
appendix
toc-brief
lov
lot
loi
loa
prologue
preface
preamble
introduction
foreword
epilogue
epigraph
conclusion
afterword
abstract
volume
part
division
chapter
frontmatter
cover
bodymatter
backmatter
CONFORMANCE
The XHTML Content Document filename SHOULD use the file extension .xhtml
It MAY include extensions to the [HTML] grammar as defined in HTML Extensions, and MUST conform to all content conformance constraints defined therein.
For all document constructs used that are defined by [HTML], it MUST conform to the conformance criteria defined for those constructs in that specification, unless explicitly overridden in HTML Deviations and Constraints.
It MUST be an [HTML] document that conforms to the XHTML syntax.
Multimedia
Media Overlay Documents (smil)
CONTENT (In this order):
1) head [0 or 1]
2) body [exactly 1]
*body
clipEnd
A clock value that specifies the offset into the physical media corresponding to the end point of an audio clip. MUST be a [SMIL3] clock value.
clipBegin
A clock value that specifies the offset into the physical media corresponding to the start point of an audio clip. MUST be a [SMIL3] clock value.
The audio element is OPTIONAL only if its sibling text element refers to audio or video media (see Embedded Media), or to textual content intended for rendering via Text-to-Speech (TTS).
*text
The text element references an element in the EPUB Content Document. A text element typically refers to a textual element, but can also refer to other EPUB Content Document media elements (see Embedded Media).
NO CONTENT
*src
The par element contains media objects which are to be rendered in parallel.
seq
The seq element contains media objects which are to be rendered sequentially.
IMPORTANT: At least one par or seq is required
par
*epub:textref
epub:textref
epub:type
head
CONTENT
0 or more elements from any namespace
NO ATTRIBUTES
epub:prefix
*version
This attribute MUST have the value "3.0".
NAMESPACE
smil
https://www.w3.org/ns/SMIL
CONSTRAINTS
The Media Overlay Document filename SHOULD use the file extension .smil.
It MUST be packaged with the EPUB Publication as shown in Packaging.
It SHOULD use semantic markup where appropriate, as described in Semantic Inflection.
It MUST adhere to the requirements for Embedded Media.
It MAY refer to more than one EPUB Content Document, but an EPUB Content Document MUST NOT be referenced by more than one Media Overlay Document.
It MUST be authored to reflect the structure of the EPUB Content Document with which it is associated, as stated in Structure.
It MUST be valid to the Media Overlays schema as defined in Appendix A, Media Overlays Schema and conform to all content conformance constraints expressed in Media Overlay Document Definition.
It MUST meet the conformance constraints for XML documents defined in XML Conformance [EPUB32].
Including in the Manifest
If an EPUB Content Document is wholly or partially referenced by a Media Overlay, then its manifest item element [Packages32] MUST include a media-overlay attribute. The attribute MUST reference the ID [XML] of the manifest item for the corresponding Media Overlay Document.
The media-overlay attribute MUST NOT be attached to manifest item elements that do not reference EPUB Content Documents.
Manifest items for Media Overlay Documents MUST have the media type application/smil+xml.
Style Information
Visual rendering information for the currently-playing EPUB Content Document element MAY be expressed in the CSS Style Sheet using author-defined classes. These author-defined class names SHOULD be declared in the Package Document metadata using the metadata properties active-class and playback-active-class. The class names are then discoverable by Reading Systems.
The active-class and playback-active-class properties MUST NOT be used in conjunction with a refines attribute [Packages32], as they are always considered to apply to the entire Rendition.
When pre-recorded narration is available for a Rendition of an EPUB Publication, Media Overlays provide the ability to synchronize that audio with the text of a Content Document (see also Aural Renditions and Media Overlays).
Text-To-Speech
Inline SSML Phonemes
The incorporation of SSML phonemes functionality [SSML] directly into a EPUB Content Document enables fine-grained pronunciation control, taking precedence over default pronunciation rules and/or referenced pronunciation lexicons (as provided by the PLS format mentioned above). Refer to SSML Attributes [ContentDocs32] for more information.
Pronunciation Lexicons
The inclusion of generic pronunciation lexicons using the W3C PLS format [PRONUNCIATION-LEXICON] enables Authors to provide pronunciation rules that apply to the entire EPUB Publication.
audio
video
General
An EPUB Content Document MUST NOT be referenced by more than one Media Overlay Document.
XHTML or SVG documents that describe the readable content and reference associated media resources (e.g. images, audio and video clips)
Content presentation should adapt to the user preferences
Designed to maximize accessibility for the visually impaired, and Reading Systems typically perform text line layout and pagination on the fly, adapting to the size of the display area, the user's preferred font size, and other environmental factors
Also supports embedded fonts
*Navigation Document (nav)
There are three types of EPUB nav elements. Specify which one is being used through the epub:type attribute
OTHER types are OK also.
hidden
*epub:type
1 of these REQUIRED
toc
Identifies the nav element that contains the table of contents. The toc nav is the only navigation aid that has to be included in the EPUB Navigation Document.
page-list
Identifies the nav element that contains a list of pages for a print or other statically-paginated source for the EPUB Publication.
landmarks
Identifies the nav element that contains a list of points of interest.
CONTENT MODEL:
HTML Heading Content
e.g. h1, h2, ....
*ol
The ol child of the nav element represents the primary level of content navigation.
*li
*span or a
A span element MUST be followed by an ol ordered list; it cannot be used in "leaf" li elements.
An a element MAY be followed by an ol ordered list representing a subsidiary content level below that heading (e.g., all the subsection headings of a section).
MUST Conform to:
It MUST conform to the content conformance constraints specific to EPUB Navigation Documents defined in EPUB Navigation Document Definition.
An XHTML Document (using the HTML nav element) to define human/machine readable navigation information.
General Info
Natively supports embedded grammars (e.g. MathML, SVG, etc)
Replaces the EPUB2 NCX Document
CONTENT (in this order):
1) metadata
2) manifest
3) spine
4) collection
collection
CONTENT (In this order):
1) metadata [0 or 1]
2) collection [1...N], or
collection [0+] link [1+]
collection link
*collection
metadata
*role
Allows grouping of logically-related Publication Resources. Enables the development of specialized content identification, processing and rendering features, such as the ability to define embedded preview content, or assemble an index or dictionary from its constituent XHTML Content Documents.
*spine
*itemref
Each itemref element MUST reference the ID [XML] of a unique item in the manifest via the IDREF [XML] in its idref attribute (i.e., two or more itemref elements cannot reference the same item). Each referenced manifest item MUST be either a) an EPUB Content Document or b) another type of Publication Resource which, regardless of whether it is a Core Media Type Resource or a Foreign Resource, MUST include an EPUB Content Document in its fallback chain.
EMPTY!
linear
no
yes
The linear attribute indicates whether the referenced item contains content that contributes to the primary reading order and has to be read sequentially ("yes") or auxiliary content that enhances or augments the primary content and can be accessed out of sequence ("no"). Examples of auxiliary content include: notes, descriptions and answer keys. An itemref that omits the linear attribute is assumed to have the value "yes".
*idref
page-progression-direction
default
The page-progression-direction attribute sets the global direction in which the content flows.
IS: An ordered sequence of ID references to top-level resources in the manifest from which all other resources in the set can be reached or utilized. The spine defines the default reading order of the given Rendition.
Provides an external declarative means to explicitly specify navigation through a collection of documents
*manifest
CONTENT:
*item
Each item element in the manifest identifies a Publication Resource by the IRI [RFC3987] provided in its href attribute. The IRI MAY be absolute or relative. In the case of relative IRIs, Reading Systems MUST use the IRI of the Package Document as the base when resolving these to absolute IRIs. The resulting absolute IRI MUST be unique within the manifest scope.
Represents a Publication Resource
ATTRIBUTES
*svg
*scripted
*remote-resources
*nav
*mathml
cover-image
media-overlay
*id
*fallback
The fallback attribute takes an IDREF [XML] that identifies a fallback for the Publication Resource referenced from the item element. Fallbacks MAY be provided for Core Media Type Resources (e.g., to provide a static alternative to a Scripted Content Document). Fallback requirements for Foreign Resources are defined in Manifest Fallbacks.
Manifest Fallback Chains
Are: A mechanism that defines an ordered list of top-level resources as content equivalents. A reading system can then choose between the resources based on which it is capable of rendering.
Identifies and describes the set of resources that collectively compose the given Rendition
*metadata
Namespace:
xmlns:dc="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/"
CONTENT Model (in any order):
link
*rel
voicing
record
alternate
acquire
OPTIONS:
xmp
The Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) is an ISO standard, originally created by Adobe Systems Inc., for the creation, processing and interchange of standardized and custom metadata for digital documents and data sets.
XMP standardizes a data model, a serialization format and core properties for the definition and processing of extensible metadata. It also provides guidelines for embedding XMP information into popular image, video and document file formats, such as JPEG and PDF, without breaking their readability by applications that do not support XMP. Therefore, the non-XMP metadata have to be reconciled with the XMP properties. Although metadata can alternatively be stored in a sidecar file, embedding metadata avoids problems that occur when metadata is stored separately.
onix
The ONIX for Books standard provides a free-to-use format for passing descriptive metadata about books between publishers, data aggregators, book retailers and other interested parties in the publishing industry. Metadata concerning one or more book titles can be stored in a suitably formatted XML file known as an 'ONIX message' ready for dissemination. Whereas other data standards exist for storing the contents of a book - the text, layout and graphics - the ONIX for Books standard holds information about the book, similar to, but more extensive than, the information one would typically find on the cover or title page of a printed book or in a library catalog. The ONIX for Books standard provides a way to communicate information about a book's author, publisher, price, publication date, physical dimensions, synopsis and many other details besides. The standard is quite extensive and most publishers currently provide only a few dozen of the many hundreds of pieces of information that the standard is designed to carry.
*media-type
*href
Linked resources are not Publication Resources and MUST NOT be listed in the manifest. A linked resource MAY be embedded in a Publication Resource that is listed in the manifest, however, in which case it MUST be a Core Media Type Resource [EPUB32] (e.g., an EPUB Content Document could contain a metadata record serialized as [RDFA-CORE] or [JSON-LD]).
Core Media Type Resource
Other
Fonts
Videos
text/css
audio/mp4
audio/mpeg
image/svg+xml
image/png
image/jpeg
image/gif
Used to attach complete
bibliographic records, etc
as part of the metadata.
*meta
scheme
*property
Any non-reserved option
Reserved Options
media:playback-active-class
media:narrator
media:duration
media:active-class
alternate-script
authority
belongs-to-collection
collection-type
display-seq
file-as
group-position
identifier-type
role
source-of
term
title-type
The meta element provides a generic mechanism for including metadata properties from any vocabulary. It is typically used to include rendering metadata defined in EPUB specifications, but MAY be used for any metadata purposes.
...
OPTIONAL ELEMENTS:
type
The [DC11] type element is used to indicate that the given EPUB Publication is of a specialized type (e.g., annotations or a dictionary packaged in EPUB format). An informative registry of specialized EPUB Publication types for use with this element is maintained in the [TypesRegistry], but Authors MAY use any text string as a value.
subject
When a scheme is identified, a subject code MUST be attached using the term property.
Authors MAY identify the system or scheme the element's value is drawn from using the authority property.
The [DC11] subject element identifies the subject of the EPUB Publication. The value of the element SHOULD be the human-readable heading or label, but MAY be the code value if the subject taxonomy does not provide a separate descriptive label.
source
rights
relation
publisher
format
date
Only one date element is allowed.
The date element MUST only be used to define the publication date of the EPUB Publication. The publication date is not the same as the last modified date (the last time the Rendition was changed). It is RECOMMENDED that the date string conform to [ISO8601], particularly the subset expressed in W3C Date and Time Formats [DateTime], as such strings are both human and machine readable.
description
creator
The [DC11] creator element represents the name of a person, organization, etc. responsible for the creation of the content of the Rendition. The role property can be attached to the element to indicate the function the creator played in the creation of the content.
coverage
contributor
The [DC11] contributor element is used to represent the name of a person, organization, etc. that played a secondary role in the creation of the content of an EPUB Publication.
*dc:language
*dc:title
*dc:identifier
urn:uuid:A1B0D67E-2E81-4DF5-9E67-A64CBE366809
NONE
General information about the EPUB Publication allowing titles, authors, identifiers, and other info to be easily accessed.
ATTRIBUTES:
xml:lang
en
Specifies the language used in the contents and attribute values of the carrying element and its descendants, as defined in section 2.12 Language Identification of [XML].
refines
Identifies the expression or resource augmented by the element.
properties
A space-separated list of property values
media-type
application/xml
id
href
absolute / relative url
dir
rtl
Right to Left
ltr
Left to Right
*unique-identifier
The primary identifier for an EPUB Publication, as identified by the unique-identifier attribute. The Unique Identifier can be shared by one or more Renditions of the same EPUB Publication. Significant revision, abridgement, etc. of the content requires a new Unique Identifier.