Definitions
Bronsted-Lowry base: must recieve an H+
Arrhenius base: gives up an OH-
pKb= -log(kb)
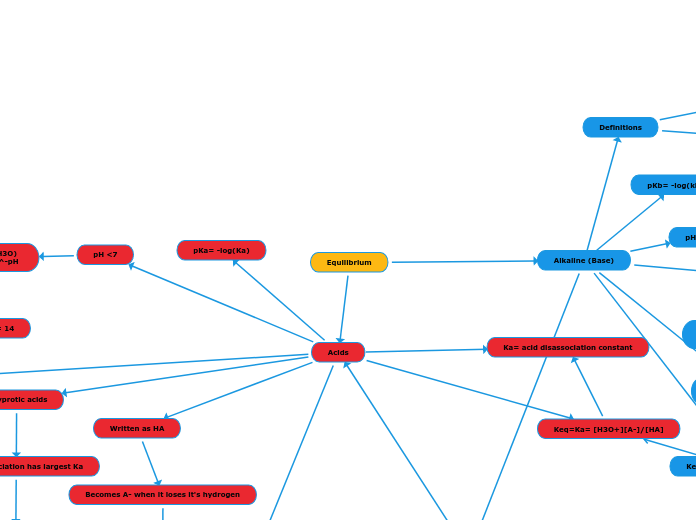
Equilibrium
Acids
Acid base titrations
(Weak acid in this example)
Buffer system
Acid added neutralizes the conjugate pair base
Base added neutralized the conjugate pair acid
pH = pKa of weak acid
Must require an acid base conjugate pair
Used to stabilize the pH of a solution
n acid=n base
Solution is neutral when this has been achieved
CaVa=CbVb
Used to find amounts of acid in a solution through neutralization
ph indicators
If done correctly, the ph indicator will change colour at the equivalence point. If not, it may change too soon, leaving the equivalence point unsolved for.
After equivalence point
Intial [OH-] from excess base
at equivalence point
Weak acid is neutralized, turns into a conjugate base
Before equivalence point
Excess weak acid
Before base is added
Disassociation of weak acid in H2O
Written as HA
Becomes A- when it loses it's hydrogen
Ha+H2O→H3O+ + A-
polyprotic acids
First disassociation has largest Ka
Next disassociation progressively has smaller Ka
Keq=Ka= [H3O+][A-]/[HA]
Ka= acid disassociation constant
pH <7
pH= -log(H3O)
(H3O)=10^-pH
pH+pOH= 14
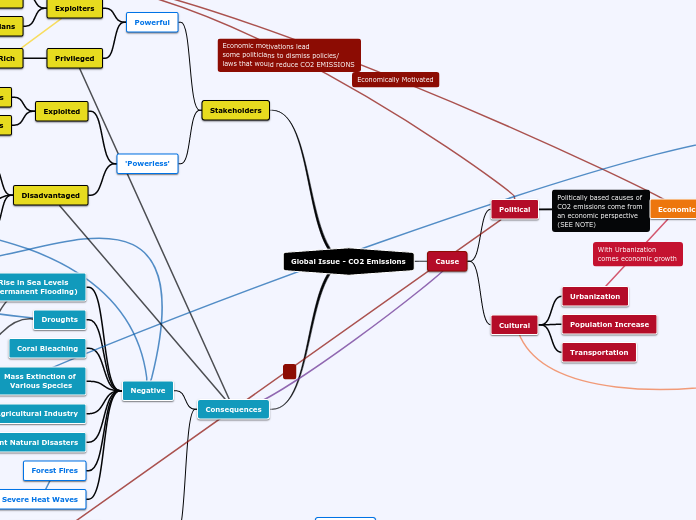
Types
Weak acids
Can calculate %disassociation... often 1%
Strong acids
100% disassociation
Ex: HCl, HBr, HI
pKa= -log(Ka)
Alkaline (Base)
Keq=Kb=[BH+][OH-]/[BOH]
Keq
Ksp
Hard vs soft water
Kidney stones
Crystallization of cations and anions.
sped up by larger surface area= faster to eq
Dissolution of salt crystals
At Eq, solids stop dissolving
common ion effect
Higher ksp= more soluble
Used on highly insoluble salts
Due to large amounts of H2O already present, we ignore H2O in Keq expressions, as it will not greatly impact the outcome of concentration.
When [P] and [R] stabilize, equilibrium is reached
Le chatelier's principle
When conditions change, eq is changed
Ex: changed in pressure, temperature are counteracted
Ex: gas exchange in the lungs
Pressure lowers, concentration lowers
Temperature speeds up forward and reverse reactions
Dynamic equilibrium
Forward and reverse actions are constant
Reactions re reversible
Easier in a closed system
phase equilibrium
Ice tables(concentrations at EQ)
Used to solve for x, using stoichiometry.
[C]^c[D]^d/[A]^a[B]^b
When Keq>1, the forward reaction is favored
When Keq<1, the reverse reaction is favored
Kf/Kr
Affected by delta H and temperature
Kb = base disassociation constant
pH >7
Conjugate pairs
Stronger acid = weaker conjugate base
Stronger conjugate base = weaker conjugate acid
pKa+pKb at 25 degrees = 14
Ka*Kb=Kw=10^-14
Connects acids and bases through the gain and loss of a proton
Ex: H2CO3 → HCO3
[OH-]= 10^-pOH
pOH= -log[Oh-]
Strong bases
Alkali metal hydroxides
(Group two) Though they have low Ksp
Lower pH and smaller Ksp
Alkali metal hydroxides
(Group one)
Highly soluble in water and high pH