by Kristin Pothoof 11 years ago
1815
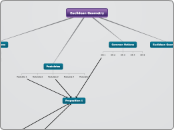
Euclidean Geometry
Euclidean geometry, established by the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid, forms the basis of classical geometry. It is built upon a set of fundamental principles that include postulates and common notions.