Molecular and Cellular Biology
Human Health
Biodiversity and the Environment
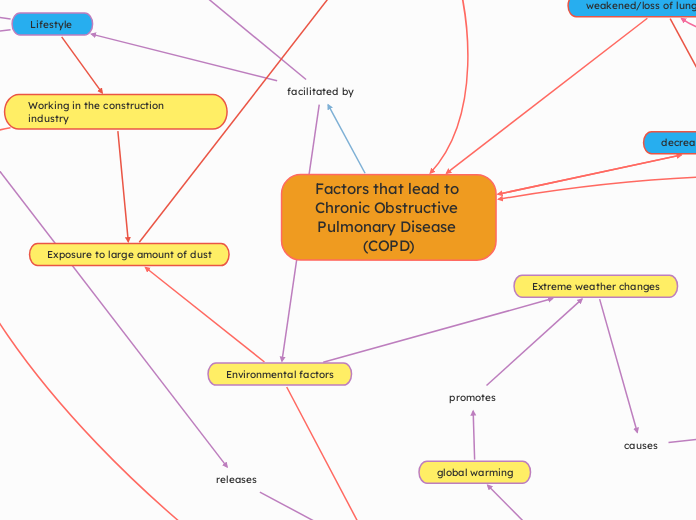
Factors that lead to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
facilitated by
Environmental factors
Extreme weather changes
Increases and decreases in temperature
result in
Huge spikes of heat patterns and intense heat exposure
leads to
Lifestyle
Poor diet
High intake of processed red meat
increases risk factors
Low intake of fruits and vegetables
less source of anti-inflammatory dietary components
that also
reduces levels of antioxidants
that can fight off
contributes to the
Working in the construction industry
Exposure to large amount of dust
Causes
Damage in alveoli
weakened/loss of lung function
decrease overall human health
Smoking
releases
harmful oxidant fumes
air pollution
can contribute to
global warming
promotes
induces
increase level of cytokines
inflammation of the lungs
activation of macrophages
excess production of proteases
Breakdown of connective tissue in lungs (Emphysema)
activation of neutrophils
Genetic factors
Coding variant in the genes of telomerase (telomere enzyme) pathway
that causes a
Genetic mutation
leads to
Telomere shortening
Increase risk of
which increases the risk of
in which
telomere are important for genetic information and is required for every cell division process)
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AAT)
encoded by
SERPINA1 gene
Variant causes
Homozygosity (inherited 2 identical forms of the gene) for SERPINA1 *Z allele (inherited 2 identical forms of the gene)
affects
Coding region
single base pair change of SERPINA1 gene
results in
substitution of a single amino acid that causes AAT polymers (proteins) to form in the hepatocytes
which is a
gene that protects the alveoli of the lung
causes
major plasma inhibitor for enzyme leukocyte elastase
located in
azurophil granules of neutrophils