by Lukas Hange 6 years ago
240
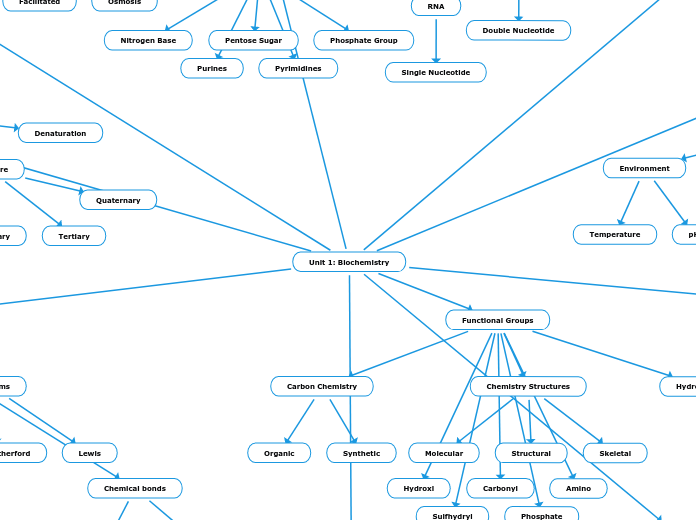
Hange Macromolecules
Macromolecules are essential biological compounds that play various critical roles in living organisms. These include lipids, nucleic acids, proteins, and carbohydrates, each with unique structures and functions.