Lecture 3
Emma Dunn + Olivia Bondy
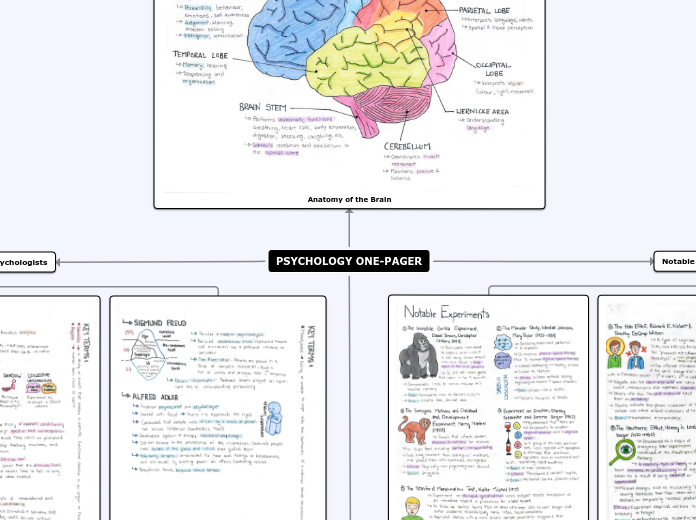
Physical Brain
Cerebral Cortex
Parietal
Primary function is spatial awarenesss and oreintation
Temperal
Primary function is to process auditory information
Frontal
Primary function is impulse controls and executive functions
Occipital
Primary function is to process vision information
The Hind Brain
Brain Stem
Cerebellum
Help coordinate movement and balanced
Midbrain
Processes vision, hearing and eye movement
Pons
Responsible for motor control and sensory analysis
Medulla Oblongata
Responsible for basic functions of body like heartbeat
Limbic System
Hippocampus
Holds long term memories
Amydgala
Considered as the brains alarm system and plays a role in emotional regulation
Hypothalamus
Controls functions of body like eating and drinking, as well as it plays a key role in your fight-or-flight reflexes
Thalamus
Information goes into the thallus and from there decides where to send it next
Neuroimaging Techniques
fMRI
Subtopic
Looks at the blood flow
in the brain to show the
activity
Stands for Functional Magnetic
Resonance Imaging
PET
Requires a radioactive
injection to view blood
flow and oxygen levels
Active parts of the brain
are displayed in hot colors
and inactive parts are displayed
in cool colours
Allows for brain activity
to be monitored during
specific events
MRI
Takes longer then
a CT Scan
More detailed view of
the brain then a CT Scan
Stands for Magnetic
Resonance Imaging
CAT/CT Scan
Stands for Computerized
Tomography
Only looks at the
structure of the
brain
Biology of The Brain
Neurotransmitters
Peptides
Endorphins
pain killer
Amines
Acetylcholine
excitatory or inhibatory
muscle contraction
Serotonin
a calming mood enhancer
Dopamine
increase pleasurable
feelings
control motor activity
Norepinephrine/Noradrenalin
arousal during stress
response
Epinephrine/Adrenaline
stress response
Amino Acids
GABA
Aspartame
Glycine
inhibitory messages
Glutamate
excitatory messages
The 3 Synaptic Connections
3) Other molecules are diffuse out cleft and are carried away as waste
2) neurotransmitters are destroyed
by enzymes
1) the axon absorbs neurotransmitter
molecules to be recycled
Nerve Cells
Neurons
Found mainly in the Central
Nervous System
Synapses
Synapses is when 2
neurons connect
A cells axon connects with
another cells dendrite
Axon
coated in a myelin sheath
They send information
to other cells
Dendrite
they carry information
to the soma
Soma
body of a nerve cell
Glial Cells
Supporting cell that help neurons
make connections
History of Brain
Trepanation
Believed to release evil spirts
that were trapped in the head
(mental illness)
boring holes into the skull to
relieve pressure
The brain has developed alot over millions of years