Lewis
In 1916, Lewis suggested that two atoms are held together in a chemical bond by sharing a pair of electrons
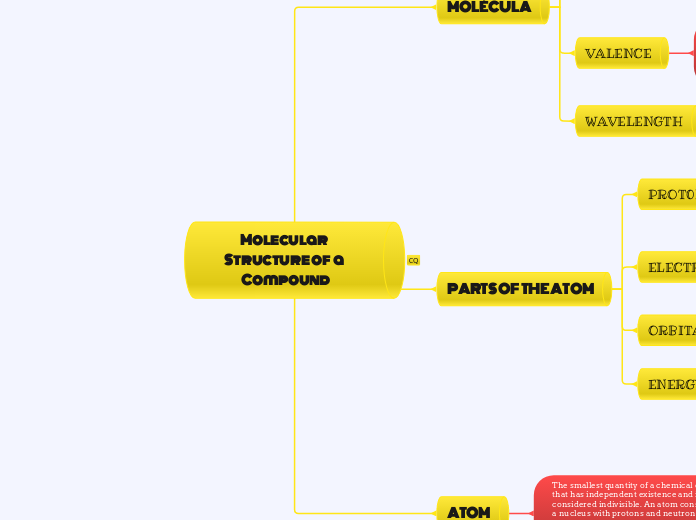
Molecular Structure of a Compound
ATOM
The smallest quantity of a chemical element that has independent existence and is considered indivisible. An atom consists of a nucleus with protons and neutrons and several orbital electrons, the number of which varies depending on the chemical element
ELECTRONEGATIVITY
It is a measure that demonstrates the ability of an atom to attract to itself the electrons that correspond to another atom when both form a chemical bond. The different electronegativity values are classified according to scales, including the Pauling scale and the Mulliken scale.
BOND
Refers to the force that holds atoms together in a molecule or compound
COVALENT
It is a type of bond that is produced between 2 atoms by the sharing of 2 or more electrons from its outer shell in order to form a stable molecule.
IONIC
It is a chemical bond between atoms, where one of them transfers an electron to the other.
PARTS OF THE ATOM
ENERGY LEVEL
Refers to a quantized state of energy that a physical system, such as an atom, molecule, or atomic nucleus, can have.
ORBITAL
Represents a region of space around the nucleus where there is a high probability of finding an electron with a specific energy
ELECTRON
A particle with a negative electric charge. Electrons form the "reactive" outer shell of atoms, interacting with others and forming chemical bonds that hold molecules together.
PROT0N
A subatomic particle with a positive elementary charge (+1), equal in absolute value and opposite in sign to that of an electron, and a mass 1836 times greater than that of an electron
MOLÉCULA
WAVELENGTH
A characteristic property of subatomic particles like electrons that exhibit wave-like behaviors due to their quantum nature
VALENCE
The number of chemical bonds an atom of an element can form to combine with atoms of other elements and create chemical compounds
RADIATION
The emission and propagation of energy in the form of waves or particles through space. It can manifest in various ways, including electromagnetic radiation and corpuscular radiation
MOL
The union of two or more atoms through chemical bonds to form a more complex and electrically neutral structure. Chemical bonds can be covalent or ionic. Source