TRANSCRIPTION
Eukarytotes
Transcription occurs in nucleus
Trancription and translation both occur in cytoplasm
Both processes can occur simultaneously
RNA Polymerase (II in Eukaryotes) binds to DNA template with help from promoter sequence
RNA Polymerase (II) adds complementary nucleotides to RNA, 5' to 3'
Mature RNA
Ribonuclease cleaves off RNA, 5' cap is added, and poly A tail is added to RNA
Spliceosomes remove introns from RNA, bind together exons to form mature RNA strand
Chromatid
H2A,H2BH3,H4 October
histone core with attached H1 linker
Unravel to expose sequences for protein/enzyme binding
Complimentary Base pairings
Double stranded
Strands are antiparallel
Each strand acts as a new template for synthesis of new strand
Double Helix
Holds Genetic material
Holds genetic material
DNA STRUCTURE
TRANSLATION
Termination
Elongation
Large Ribosome
A- Amino Acyl Transferase
Continuous Codon Cycle being added
Adds Codons
P- Peptidyl Transferase
Creates Peptide Bonds
Creates Polypeptides
Made in a start N-C end
Synthesized by Free Ribosomes
Free Ribosome are incomplete in synthesizes
Travels Through Vesicles
Endomembrane System
To enter a ER Signal Molecule is required
SRP which Binds to SRP Receptor on free ribosomes produces proteins
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Secreted using Secretory Pathway
Exocitized
Outside of the cell
Can add a glycoprotein/ Known for chemical modifications
Free ribosomes are complete in synthesis
Plastids/ Chloroplast
Perioxisomes
E-Exit
Releases Codons
5' ---AUG---3'
Small Ribosome
Initiation
Prokaryotes start with a formal MET and Eukaryotes do NOT
Semi Conservative
Hydrogen Bonds
Chromosomes
Nucleosomes
DNA +histone core
eptor
Form NADPH from NADP+
GO DOWN ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
Electrons are also fed here from water after O2 is released
Electrons get excited and get grabbed by electron acceptor molecule
Cycle continues until reached by main reaction center pair of chlorophyll a
Energy is then aborbed by the next molecule
Fluorescence
Protons cause an afterglow
When pigment molecules absorb light, electrons get excited and unstable
When electrons fall back down, they release absorbed energy
Is the first photosystem used for noncyclic flow
Transfer of electrons down the Electron transport chain
Ligand is the 1st messenger
absorbs light at 700 nm
Absorbs light at 680 nm
Reaction-center complex with light harvesting complexes
Added phosphate group to ADP
Photophosphorylation
Generates ATP
When excess NADPH is present, PSI is used to produce ATP instead, quickly
Cyclic flow
Noncyclic Flow of electrons
Photosystem I
Energy is passed between molecules after light photon is absorbed like in PSII until reaching Chlorophyll a molecules and grabbed by electron acceptor
Electrons go through electron transport chain again but to Ferredoxin
Photosystem II
Convert solar energy to chemical
Thylakoids of chloroplast
Calvin cycle
Regeneration of CO2 acceptor
Reduction
Subtopic
Outside thylakoid in stroma
Openings on leaf surface that allows CO2 to enter and O2 leaves
Light reactions
Mesophyll tissue
Stomata
Leaves
Photosynthesis
Maximum ATP produced per molecule of glucose: 30 or 32
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ----> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
Energy and Cell Communication
Cell Signaling
Gene Expression
Enzymes
Substrates
Cooperativity
Substrate binds to 1 of the present active sites
Binding of 1 causes change in all of the rest/ cause the rest to become active
Activators and inhibitors
Allosteric
Binds to the NON- active site
No prod can be formed from adding more substrate
Enzyme is changed shape to accomodate the allosteric inhibitor/activator
Competitive
Fights/ Blocks for active site
Product is formed from adding more substrate
G- Protein Coupled Receptor
G- Protein is coupled with GDP and rests as in an inactive state.
Ligand reaches G- Protein Receptor
GTP ("a form of ATP") binds to the G-protein receptor while the Receptor changes shape causeing the G-protein to simultaneously release GDP.
The G-protein slides across the membrane towards the enzyme Adenyl Cyclase
Once it reaches and binds to the enzyme, it uses a phosphate from GTP (ATP) to produce cAMP.
GTP reverts back to GDP using Phosphatase to break off a phosphate
Travels back across the membrane with GDP to bind to the G-Protein receptor
cAMP- Cyclic AMP
Removes phosphates using the enzyme Phosphosdiesterase
1st protein Kinase activated
cascade
2nd Protein Kinase activates
Protein Kinase 3
protein Kinase 4
Protein Kinase 5
etc
Mutation
The enzyme Phosphodiesterase doesn't stop cell growth or cAMP is still active
Cancer- continuous overgrowth of cells
Dna Transcription, Protein synthase, Cell Growth, etc is signaled to start producing
2nd Signal molecule/ messenger
Produces AMP
Cell Signaling Pathway
Step 1: Small Non-Polar molecules (Such as steroids) pass through the cell membrane
Step 2: The signal molecule reaches the receptor which binds/ conforms to the signal molecule
Step 3: The signal molecule and the receptor has confirmation to pass through the nuclear pores on the nuclear membranes
Step 4: Activates gene expression
Simple Diffusion
Cell Respiration
Glycolysis
Makes ATP through substrate level phosphorylation
Occurs in cytoplasm of cell, occurs in two phases
Through several reaction, 2 NAD+ is turned into 2 NADH and 4 ADPs are turned into 4 ATP. 2 molecules of water are also released.
Net: 2 NADH, 2 ATP
NADH formed in all reactions are used in electron transport chain
End result of glycolysis: 2 Pyruvates
Step 1: Hexokinase takes phosphate group from ATP and gives it to Glucose, to form Glucose 6-phosphate
Step 3: Phosphofructokinase gives Fructose 6-phosphate a phosphate from ATP. So far 2 ATP have been used.
Anaerobic
Lactic Acid
breaks down carbohydrate to use energy when oxygen levels are low
Anaerobic processes occur without the presence of oxygen
Aerobic
Pyruvate Oxidation
No ATP produced
Takes 2 molecules of pyruvate from glycolysis and forms 2 Acetyl CoA
2 molecules of CO2 and NADP are formed and released
Citric acid cycle (Krebs Cycle)
Electron transport chain
Net result: 26 or 28 ATP
Oxidative phosphorylation
NADH and FADH2 give up their electrons to a less electronegative carrier
Electrons move down chain to increasingly electronegative carriers, releasing energy through each transition
Electrons end up meeting oxygen at the end of the chain to form water
Energy released is used to pump protons against their concentration gradient into inner membrane space
Chemiosis
Protons are able to flow down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase, which provides the energy needed to add a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP
Occurs in inner membrane space ad miochondrial matrix
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Acetyl CoA changes oxaloacetate into citrate
Water is released, citrate is changed into isocitrate
Isocitrate is oxidized, NADH is reduced to form alpha ketoglutarate. CO2 is released
More reactions occur, end result is Malate being oxidized to form oxaloacetate and the cycle continues
Net result: 3 NADH, 1 ATP, 1 FADH2
Occurs in mitochondira
Aerobic process occur in the presence of oxygen
falls below the carbon ring
falls above the carbon ring
Building blocks of carbohydrates
Beta glucose
Chitin
Cellulose
Dextran
Glycogen
Amylose
Amylopectin
Starch
Alpha glucose
Glycosidic linkage
Structure (stability)
Disaccharide synthesis
Polysaccharide
Glucose
Fructose
Storage
Energy production, energy storage
Monosaccharides
Carbohydrates
Biomolecules
Cytoplasm
Fluidity
Aids in fluidity due to unsaturated fats. Unsaturated fats have a bent/kink tail due to cis double bonds. The kinks causes other phospholipids to be more spread out allowing proteins and other molecules to pass through easier.
Bilayer with hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads
Polymers
Nucleic Acids
Monomers
Nucleotides
Sugar
Nitrogenous Base
Purines
Guanine (G)
Adenine (A)
Pyrimidines
Thymine (T)
Uracil (U)
Cytosine (C)
Phosphate Group
connects nucleotides
Phosophodiesters Bonds/Linkage
Condesation/ Dehydration reactions occur
Takes away a water (H20) molecules and bonds/combines what is left
the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid. They form between the 5' and 3' ends of two different nucleotides forming an ester linkage.
Process which a polypeptide chain folds to become a active proteins in its 3D structure.
Quaternary
Two or more tertiary structures come together through interactions between the R groups
Tertiary
Polypeptide begins to fold as R groups interact with each other
Ionic bonding between charged R groups
Disulfide bridge (Only covalent bond between R groups)
Hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar R groups
Secondary
Hydrogen bonding occurs between carboxyl and amino groups within the polypeptide
Alpha Helices and Beta pleated sheets
Primary
Amino acids peptide bonded with each other to create a polypeptide chain
Protein Folding/Protein Synthesis
The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell which means that it produces ATP(Energy). Although, the mitochondria isn't the cite where energy is created, but rather it is harnessed.
ER
Smooth
Produces lipids and phospholipids which make up the cell membrane
Rough
Has ribosomes connected to its membrane, facilitates protein synthesis and folding
Plants
Cytoskeleton
Gives the cell structure, shape, and scaffolding.
Central Vacuole
Storage place for plant cells. Fills with water and food. When filled, creates turgor pressure within the cell, giving it a turgid structure.
Chloroplasts
Responsible for the photosynthesis
Proteins
Mitochondria
Cell wall
Bacteria
Peptidoglycan
Polysaccharide made up of amino acids that form the cell wall of many bacteria
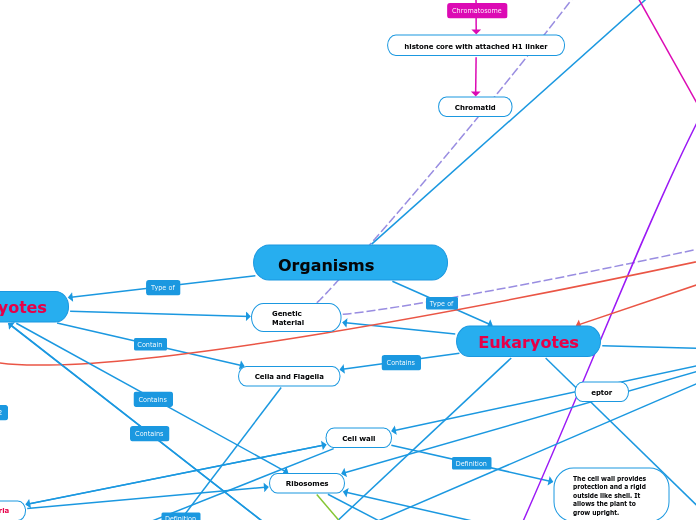
The cell wall provides protection and a rigid outside like shell. It allows the plant to grow upright.
Organisms
Eukaryotes
Plasma Membrane
Lipids
Energy Storage
Triglycerol/Tryglyceride/Glycerol
3 Fatty Acids
Ester Linkage
Dehydration/ Condensation between the O's and C's of a fatty acid chain
Fat molecule
Saturated
Solid at room temperature
Hydrogenation
Chemical process/ reaction that bonds fats with saturated fats
No double Bonds; Every possible location is bonded with an Hydrogen
Unsaturated
Liquid at room temperature
Trans Fats
Hydrogen Bonds are on opposing vertical (diagonally) sides
Cis Fats
The Hydrogen bonds are on the same vertical side
Double Bonds
Cholesterol
Help with the fluidity of the membrane
LDL/ Low Density Lipoprotein
Bad Cholesterol
Saturated fats and trans fats can increase LDL
HDL/ HighDensity Lipoprotein
Good Cholesterol
Phospholipids
Amphiphatic Bilayer
Hydrophilic Head and Hydrophobic tail creates a membrane
Steroids
4 Fused rings of carbon and the precursor of sex hormones
Boundary of cell, separates everything within the cell and the environment
Prokaryotes
Archaea
Extremophiles
Thermophiles
Thrive in very Hot environments
Halophiles
Highly saline environments
ability to live in extreme environments
Celia and Flagella
A variety of functions across different types of cell, but are usually used for movement and mating
Genetic Material
DNA/ Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
Mutations
Nonsense
Prematurely stops/ early stop codon
Frameshift
1-2 Nucleotides are removed/added
Missence
There's a change in the amino acid Codon
Silent
There's a change in the nucleotide, but there is no change in the codon
Dna provides directions for its own replication. It also directs synthesis RNA (mRNA) and, through mRNA, controls protein synthesis, a process gene expression
Double stranded with complementary base pairing. C-G; T-A; A-U; These are bonded through hydrogen bonds. DNA is also in the shape of a double helix.
RNA/ Ribose Nucleic Acid
Self- Replicatiing RNA helped jumpstart evolution
Single strand of DNA; takes a role in the expression of genes
Animals
Centrosomes
Aids in cell division
Peroxisomes
Have oxidated reactions (peroxides) and have very similar storage and digestive like functions. They basically help prevent oxygen in the cell.
Lysosomes
Break down materials within the cell. Digestive system of the cell. Helps with recycling materials
Ribosomes
Performs biological protein synthesis. Links amino acids together to form polypeptide chains.
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Region of nucleus where ribosome synthesis occurs
Nuclear Envelope
Separates Nucleus from cytoplasm and holds nucleus. It is the "plasma membrane" of the nucleus.
Membrane bound organelle that contains the genetic material of the cell.