by Ingrid Nathalia Tobar Tobar 3 years ago
389
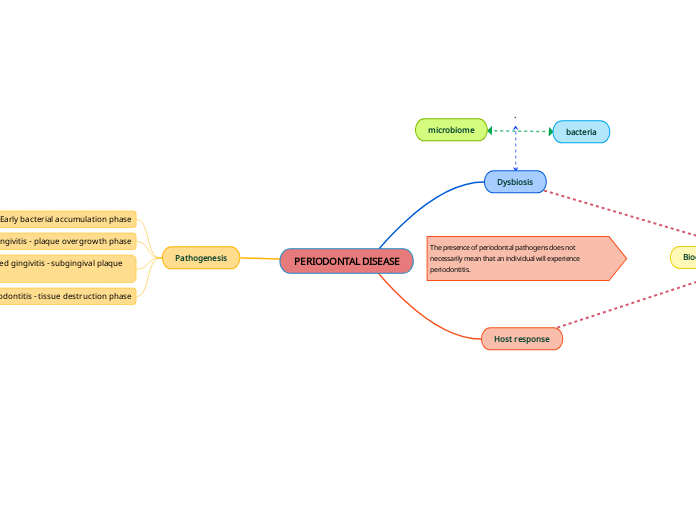
PERIODONTAL DISEASE
The progression of periodontal disease involves a series of phases, each marked by distinctive microbial activity and immune responses. Initially, bacteria accumulate, leading to an overgrowth of plaque, which is characteristic of early gingivitis.