Shimer-Macromolecules
Lipids
Fats
Saturated Fats
Solid at Room Temperature
Long, Straight Chains
No C=C double bonds
All C's bonded to H's
Unsaturated Fats
(Actual Chain is Bent)
Vegetable Oils
Liquid at Room Temperature
Plant and Fish Fats
Bend in chain
C=C double bonds
Non-Polar and Hydrophobic
Fats, Oils, Phosphlipids, Steroids
Structure of a Phospholipid
Phospholipids are found in the cell membrane
Energy Storage, Cushions Organs, Insulates Body
Triglyceride
Proteins
When a protein loses its shape it is called DENATURING
Temperature and pH can denature a protein
Peptide bonds are the special bonds that keep them together
The R group changes between them to make them unique
The shape allows proteins to do their jobs
There are four different layers of Proteins
Muscle, Skin, Hair, Enzymes
Hormones, Movement in Muscles, Immune System, ENZYMES, Transport
Amino Acid
Carbohydrates
Cellulose in Nature: Structure in plants (cell walls)
Cellulose in American Diet: Fiber
Pants-Starch, Animal-Glycogen
Glucose,Fructose, Sucrose, Maltose
Sugars end with -OSE
Sugars, Starches, Cellulose, Glycogen
Carbon Ring(Hexagon)
Energy Storage, Quick Energy, Structure
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Monosaccharide
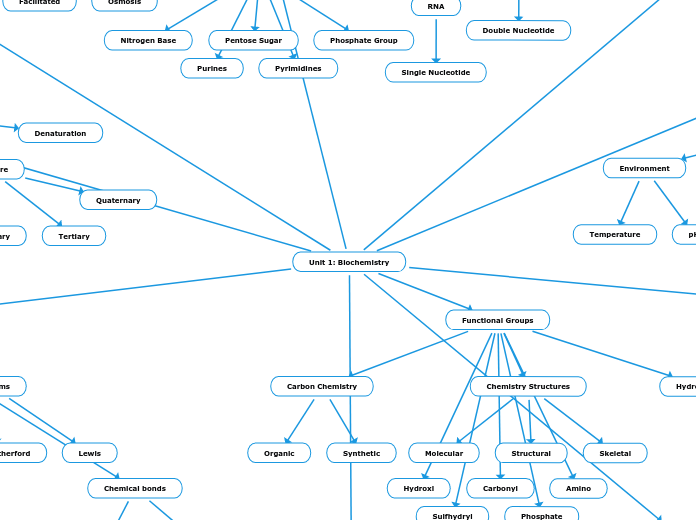
Nucleic Acids
Phosphate Group, Nucleotide, and a Pentose Sugar make up a Nucleic Acid
Stores and Transmits Hereditary Information
RNA and DNA
RNA is a single nucleotide chain and DNA is a double nucleotide chain (double helix)
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, AND Nitrogen
Nucleotide