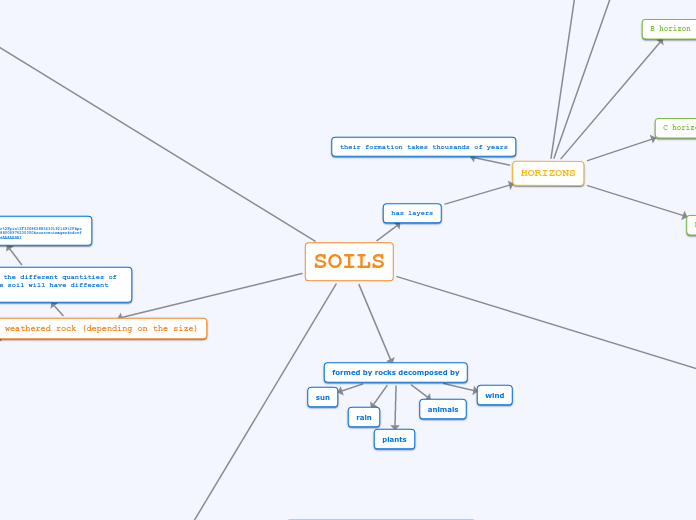
SOILS
formed by rocks decomposed by
plants
animals
wind
rain
sun
factors that influence soil formation
CL.O.R.P.T
T: time
with enough time, soil becomes more developed
P: parent material
R: relief
change in elevation
O: organism
CL: climate
rainfall, temperature and humidity
Division of soils
VERTISOL
-dry out regularly
makes soil "break"
makes it impossible for horizons to be formed
-have a lot of clay on them
HISTOSOL
unstable and dangerous to build on
-highly acidic
-wetland soils
ANDISOL
-rich in nutrients
-volcanic soils
OXISOL
.very developed horizons
-rainforest soils
MOLLISOL
.grassland soils
-darkest and most fertile soil
ARIDISOL
-dessert soils
(not sandy desserts)
ULTISOL
-subtropical locations
-lots of iron
ALFISOL
-usually under broadleaf and decidious forest
-rich in iron and aluminum
SPODOSOL
-low fertility
-acidic due to pine needles
-in coniferous and boreal forests
GELISOL
-little horizon development
permafrost
-at high latitudes
INCEPTISOL
-sligtly more horizon development
ENTISOL
-most common type on Earth
-very young
-no horizons
has layers
HORIZONS
R horizon
just rock
C horizon
composed by large rocks and gravel
where bedrock is slowly degrading into soil
B horizon
furthest roots go
subsurface
A horizon
where living organisms are
also called "biomantle"
O horizon
where dead plant matter is
their formation takes thousands of years
3 types of weathered rock (depending on the size)
depending on the different quantities of each one, the soil will have different properties
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.pinterest.fr%2Fpin%2F326862885430192149%2F&psig=AOvVaw2TvjjBt0YkwAvPXNKvfFOj&ust=1588008976230000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAIQjRxqFwoTCIDD3snQhukCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAI
silt (medium)
sand (biggest)
clay (smallest)
Formed by weathering and erosion
erosion: When smaller rocks are carried away from parent rocks
because of wind or water
weathering; Is the breaking of rocks into smaller rocks
by a physical or chemical process