by Marcela Costa 2 years ago
191
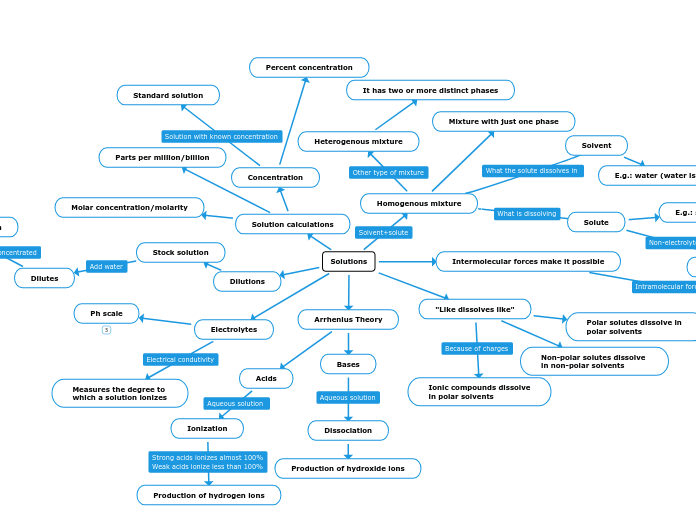
Solutions
In chemistry, the concept of solutions is fundamental, involving the formation of homogeneous mixtures where solutes are uniformly distributed within solvents. Concentration measures such as molarity, percent concentration, and parts per million are pivotal in quantifying the amount of solute in a solution.