STRUCTURE OF PROTEIN
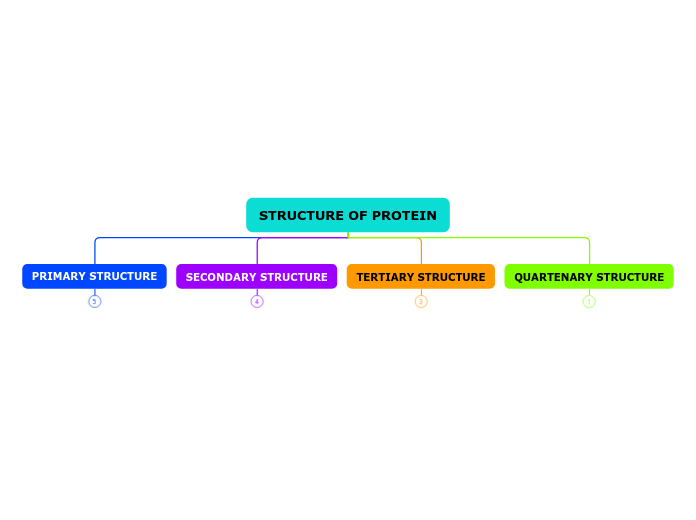
QUARTENARY STRUCTURE
Protein that has more than one polypeptides has a quaternary structure
TERTIARY STRUCTURE
Is referred as the highly specific 3-D configuration of protein
Four types of bond are involved:
a. Disulphide bonds
b. Ionic bonds
c. H-bonds
d. hydrophobic interactions
These bonds stabilize the 3-D configuration of the protein
SECONDARY STRUCTURE
This refers to the unique way of certain protein fold into a 3-D
structure which is stabilized by H-bonds only
2 common types of secondary structure:
- Alpha-helix
- Beta-pleated sheet
Beta - Pleated Sheet
Alpha - Helix
PRIMARY STRUCTURE
Protein molecules are composed
of large number up to 20 different
amino acids joined together by peptide linkages
Subtopic
Primary Structure is defined as:
It is the determination of the sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chains.
All amino acids have amino
group (NH2) and a carboxyl
group (COOH)