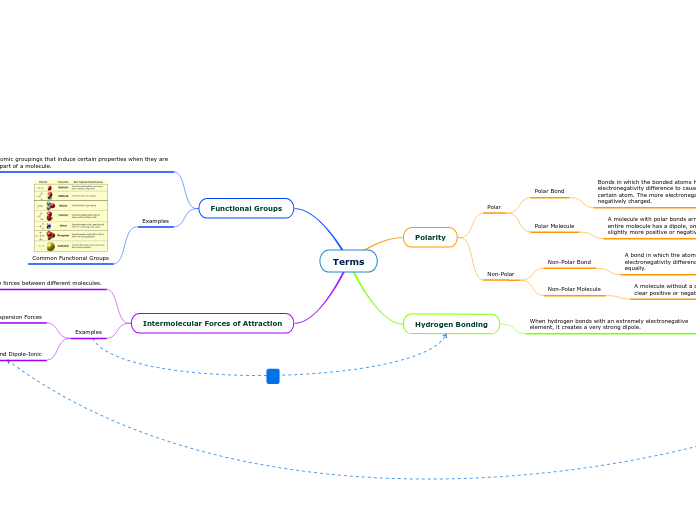
Terms
Intermolecular Forces of Attraction
Dipole-Dipole and Dipole-Ionic
Polar molecules and ionic compounds have a positively and negatively charged side. Positive sides of a molecule will attract to negative sides of another molecule and vice versa.
London Dispersion Forces
Electrons are not always evenly distributed around atoms, moments in which there are more electrons in an area will create a negative charge, attracting positively charged objects. Similarly, the lack of electrons in an area will create a slight positive charge
Attractive or Repulsive forces between different molecules.
Functional Groups
Examples
Common Functional Groups
Atomic groupings that induce certain properties when they are a part of a molecule.
Hydrogen Bonding
When hydrogen bonds with an extremely electronegative element, it creates a very strong dipole.
"Very electronegative element" is usually oxygen, fluorine, or nitrogen.
Polarity
Non-Polar
Non-Polar Molecule
A molecule without a dipole. The molecule does not have a clear positive or negative side.
Non-Polar Bond
A bond in which the atoms do not have a significant electronegativity difference. Electrons “favor” both atoms fairly equally.
Polar
Polar Molecule
A molecule with polar bonds arranged in a way so that the entire molecule has a dipole, one side of the molecule is slightly more positive or negative than the other.
Polar Bond
Bonds in which the bonded atoms have a sizable enough electronegativity difference to cause electrons to “favor” a certain atom. The more electronegative atom will be slightly negatively charged.