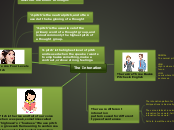
Correlational Feature 1: German and Hungarian individuals are angry due to their low frequency pitch
Correlational Feature 2: Danish individuals have no feelings since their pitch is middle ground which makes them sound monotone
Correlational Feature 3: Males have an authoritative voice due to their lower voice frequencies.
Misconception via undergeneralization: All Asian cultures are high frequency voice tones.
Misconception via overgeneralization: All females have a higher pitch frequency in their voices.
Non-Examples: Female U.S. and Female U.K.
Prototypes: Hungarian/Chinese and Finnish/Danish
Voices in different languages
Narrowed Down: The pitch, tone, and frequency of speaking in different languages are interpreted very differently to someone who does not speak that language.
Defining Features: Finding the exact frequency of an individual speaking and determining their mood and intention solely from the frequency pitch.
Example 3: Female U.S. speakers have a 10hz higher score than European females causing U.S. females to sound happier.
Example 2: Finnish speakers have a very low frequency whereas Danish speakers are more middle ground.
Example 1: Hungarian pitch is low and Chinese pitch is high, difference measuring about half an octave difference on a piano, the Hungarian person sounds angry and the Chinese person.
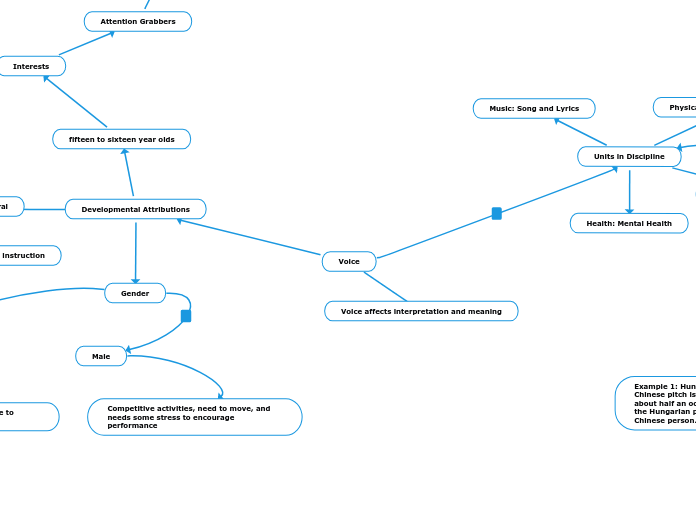
Voice
Units in Discipline
Music: Song and Lyrics
Physical Science: Communication
Language Arts: Public Speaking
Health: Mental Health
Developmental Attributions
fifteen to sixteen year olds
Interests
Relevance
Group Work
Needs communication with peers
Attention Grabbers
Needs breaks and allow for deviations from the main topic
Gender Neutral
Vygotsky
Use the "zone of proximal development" to further knowledge and teach one another through social interaction.
Piaget
use the knowledge students already have to form opinions and allow students to accommodate new ideas.
Needs clear and direct instruction
Gender
Male
Competitive activities, need to move, and needs some stress to encourage performance
Female
Social interaction needed, sensitive to noise, needs a calm atmosphere
Voice affects interpretation and meaning