Final
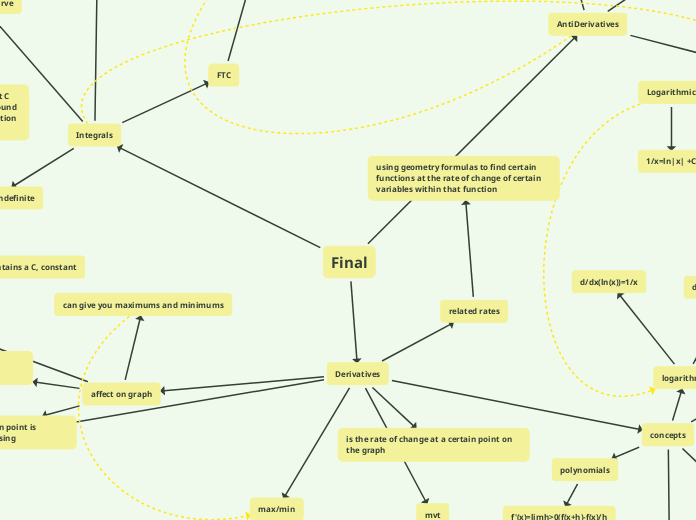
Derivatives
mvt
as long as a function is differentiable and continuous than the derivative can be used to see that c exists on (a,b)
max/min
minimums can be determined where the derivative at a certain point =0, the point before being negative and the point after being positive
maximums can be determined where the derivative at a certain point =0, the point before being positive and the point after being negative
related rates
using geometry formulas to find certain functions at the rate of change of certain variables within that function
implicit differentation
can be used to find the slope at a certain point in a graph
used to find the derivative of equations not written in terms of one variable
affect on graph
concavity
found using the derivative of the derivative
if at a point on the 2nd derivative the value is positive the function is concave up
if at a point on the 2nd derivative the value is negative the function is concave down
if the derivative at a certain point is positive the slope is increasing
if the derivative at a certain point is negative than the slope is decreasing
can give you maximums and minimums
concepts
trig
logarithmic
d/dx(loga(x))=1/xln(a)
d/dx(ln(x))=1/x
chain rule
F'(x)=f'(g(x))g'(x)
inverse trig
http://www.beyondcalculus.com/derivatives/functions.html
Product rule
d/dx(f(x)*g(x)= f'(x)*g(x)+f(x)*g'(x)
Quotient rule
d/dx(f(x)/g(x))= (f'*g-f*g')/g(x)^2
exponential
d/dx(b^x)=b^x*ln(b)
polynomials
f'(x)=limh>0(f(x+h)-f(x)/h
is the rate of change at a certain point on the graph
Integrals
Net Change Theorem
area under curve
can be used to find net area under a cover from (a,b)
finding antiderivate of inside function of integral then finding F(a)-F(b)= the net area
definite vs indefinite
Definite solution does not contain that C rather an exact constant and can be found by knowing an exact point on the function and filling it in.
indefinite solution contains a C, constant
FTC
if the function is defined between (a,b) then the integral if the function is the antiderivative
AntiDerivatives
+C, the constant
is apart of the general solution
rules
kdx=kx+C
x^n=1/n+1x^n+1+C
e^ax=1/a*e^ax+C
b^x=1/lnb*b^x+C
Logarithmic
1/x=ln|x| +C
exact opposite of derivative
could just be opposite of the derivative but dont forget the +C